When something goes wrong in an organization, the first question that is often posed is, “Whose fault is it?” When there’s data missing in accounting, it’s the bookkeeper’s fault. If we lose a key customer, it’s the sales group’s problem- “They promised more than we could deliver!”
When errors such as these surface, blaming seems to be a natural reflex in many organizations. Even those individuals who wish to learn from mistakes fall into naming culprits. Once we figure out who’s at fault, we then try to find out what is wrong with the supposed offenders. Only when we discover what is wrong with them do we feel we have grasped the problem. Clearly they are the problem, and changing or getting rid of them (or simply being angry at them) is the solution.
There’s a problem with this common scenario, however: Where there is blame, there is no learning. Where there is blame, open minds close, inquiry tends to cease, and the desire to understand the whole system diminishes. When people work in an atmosphere of blame, they naturally cover up their errors and hide their real concerns. And when energy goes into finger pointing, scapegoating, and denying responsibility, productivity suffers because the organization lacks information about the real state of affairs. It’s impossible to make good decisions with poor information.
In fact, blame costs money. When the vice president of marketing and the vice president of R&D are blaming each other for quality problems in product development, they can’t focus on working together to bring the best products to market. Their finger pointing results in lost sales potential.
Blame rarely enhances our understanding of our situation and often hampers effective problem solving. So how do we avoid the tendency to blame and create organizational environments where we turn less frequently to blame? Clarifying accountability is one option. This process of assigning responsibilities for a situation in advance can help create a culture of real learning.
Accountability comes from clear contracting, ongoing conversations, and an organizational commitment to support accountability rather than blame. The contracting focuses on tasks to be accomplished, roles to be taken, processes to be used, standards sought, and expected results. Periodic conversations over time review both explicit and tacit contracts in order to verify shared understanding. This communication becomes most useful when people are willing and able to discuss their common difficulties within a larger setting that values accountability.
The Differences Between Accountability and Blame
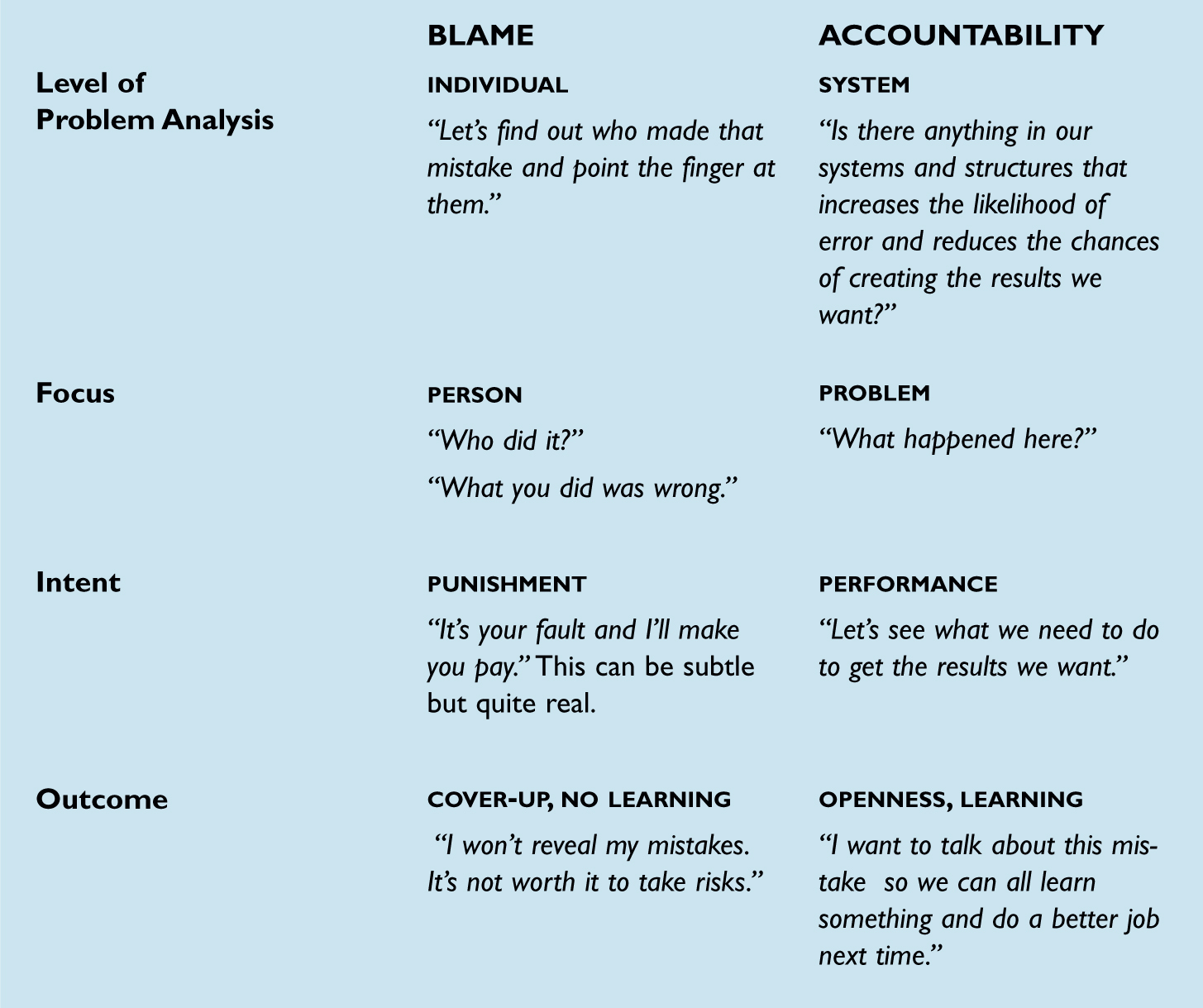
The dictionary helps clarify the differences between accountability and blame. To be accountable is “to be counted on or reckoned on.” To blame is “to find fault with, to censure, revile, reproach.” Accountability emphasizes keeping agreements and performing jobs in a respectful atmosphere; blaming is an emotional process that discredits the blamed.
A focus on accountability recognizes that everyone may make mistakes or fall short of commitments. Becoming aware of our own errors or shortfalls and viewing them as opportunities for learning and growth enable us to be more successful in the future. Accountability therefore creates conditions for ongoing, constructive conversations in which our awareness of current reality is sharpened and in which we work to seek root causes, understand the system better, and identify new actions and agreements. The qualities of accountability are respect, trust, inquiry, moderation, curiosity, and mutuality.
Blaming, on the other hand, is more than just a process of allocating fault. It is often a process of shaming others and searching for something wrong with them. Blaming provides an early and artificial solution to a complex problem. It provides a simplistic view of a complex reality: I know what the problem is, and you’re it. Blame thus makes inquiry difficult and reduces the chances of getting to the real root of a problem. Blame also generates fear and destroys trust. When we blame, we often believe that other people have bad intentions or lack ability. We tend to excuse our own actions, however, because we know firsthand the challenges we face. The qualities of blame are judgment, anger, fear, punishment, and self-righteousness.
The Organizational Consequences of Blame
Blame Slows Information Flow and Reduces Innovation. People sometimes use blame as a strategy to get others to take ownership of problems. But this approach often backfires because people begin to equate acknowledging mistakes and surfacing bad news with punishment. When this happens, two reinforcing sets of behaviors may emerge: one by managers who are ostensibly seeking information and then punishing those who bring bad news, and the other by groups of employees who hide information and try either to protect each other or to blame each other. People who feel compelled to protect themselves can’t admit mistakes-and therefore can’t learn from them. Under these conditions, individuals spend time denying problems rather than solving them, and
The Reinforcing Cycles of Blame
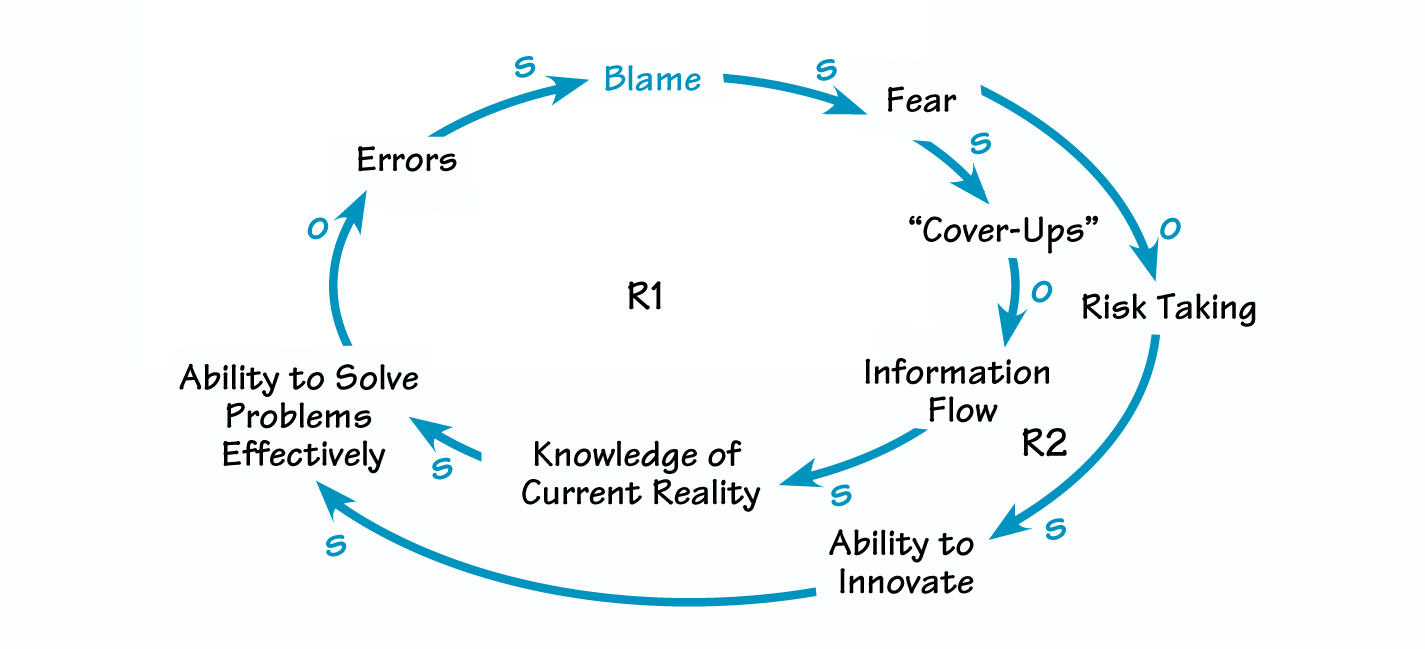
Blame causes fear, which increases cover-ups and reduces the flow of information. The lack of information hinders problem solving, creating more errors (R1). Fear also stifles risk taking and discourages innovation (R2).
As shown in “The Reinforcing Cycles of Blame,” blaming leads to fear, which increases cover-ups and reduces the flow of information by stopping productive conversation. The lack of timely and accurate information about an organization’s current reality hinders problem solving, leading to more errors and more blame (R1).
Blaming and the fear it generates also discourage innovation and creative solutions. Frightened people don’t take risks, which are essential for innovation. Lack of innovation, in turn, leads to an inability to solve problems effectively and an increase in errors (R2).
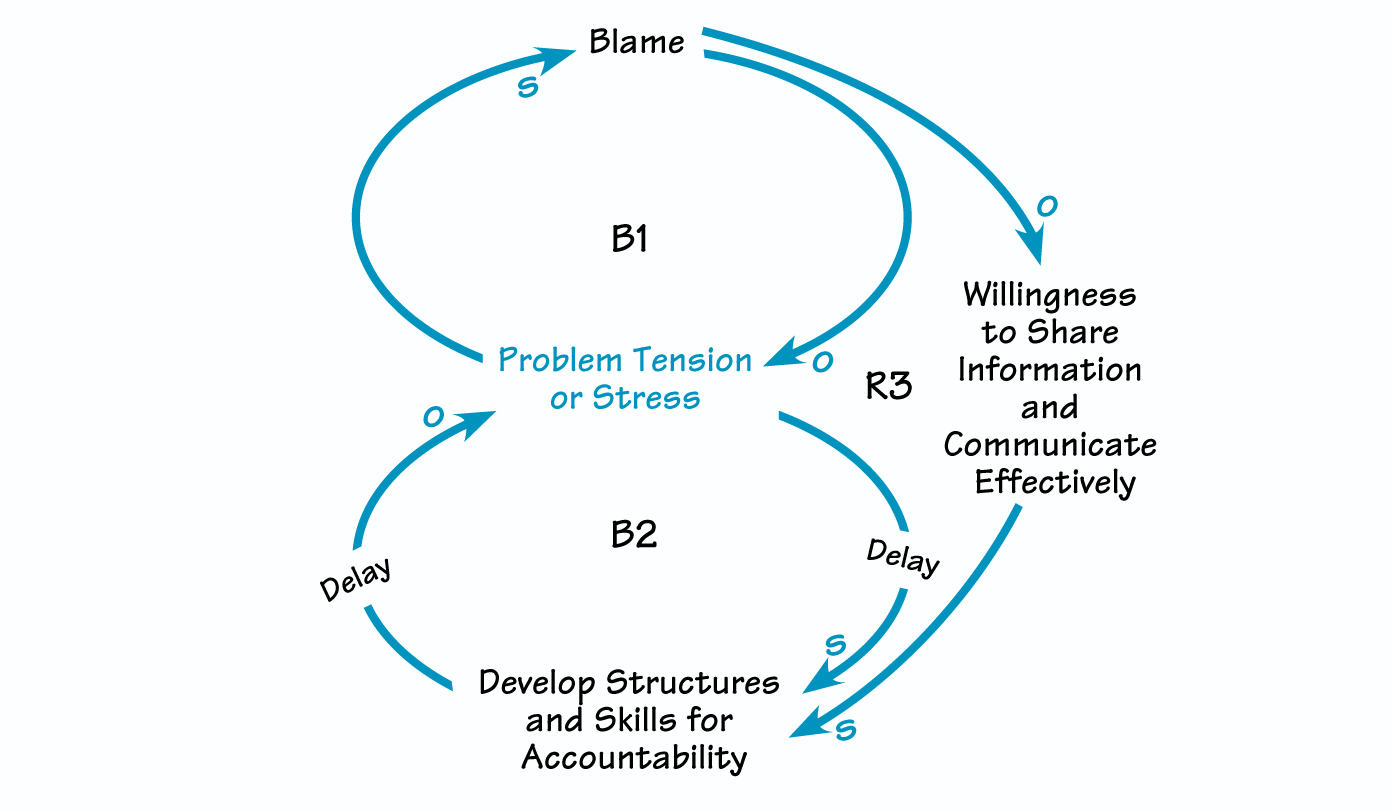
Blame “Shifts the Burden.” In a “Shifting the Burden” situation, a problem has multiple solutions. People often grab onto the most obvious, short-term fix rather than search for the fundamental source of the problem. The lack of a permanent, long-term solution reinforces the need for additional quick fixes. Blame is a fix that actually diverts the blamers’ attention away from long-term interpersonal or structural solutions to problems (see B1 in “The Addiction to Blame” on p. 3). Although blame provides some immediate relief and a sense of having solved a problem (“It’s their fault”), it also erodes communication (R3) and shifts the focus even further from accountability (B2), the more fundamental solution.
Blaming can also be addictive, because it makes us feel powerful and keeps us from having to examine our own role in a situation. For example, Jim, a brewery manager, got word that things were slowing down on line 10, a new canning line. He left his office and headed to the plant floor. “Grady, you’ve got to get this line going. Get with it,” he told his line foreman. Grady replied, “Jim, you know those guys on the last shift always screw things up.”
This is a familiar conversation to both men. Each walks away thinking something is wrong with the other. Jim thinks, “That Grady, I give him responsibility and he just can’t get it together.” Grady thinks, “Why is he always on my case? Can’t he see this is a tough issue? He’s so simplistic and short-sighted.”
In this scenario, Jim can walk away feeling relieved because he knows what the problem is-Grady is a lousy supervisor and may need to be replaced. Grady, on the other hand, can blame Jim for being a shortsighted, run-the-plant-by-the-numbers manager. Both get some initial relief from blaming each other, but neither solves the ongoing problem.
Moving from Blame to Accountability
How, then, do we move from blame to accountability? Even within carefully designed systems, people may fail at their work. And even with a knowledge of system dynamics, we still often look for an individual’s failure as a way to explain a problem. One leverage point is to understand the organizational dynamics of blame as described above. There is also leverage in changing how we think about and conduct ourselves at work.
There are three levels of specific behavioral change in moving from blame to accountability-the individual level, the interpersonal level, and the group or organizational level. First, individuals must be willing to change their own thinking and feelings about blame. Second, people need to become skillful at making contracts with one another and holding each other accountable for results. Third, groups need to promote responsible and constructive conversations by developing norms for direct conflict resolution between individuals. These behavioral changes-and the use of systems thinking to focus on the structures involved and not the personalities-can help create a constructive organizational culture.
Individual Level
Below is a list of ways to start breaking the mental models we hold about blame. When you find yourself beginning to blame someone else for a chronic problem, refer to this list and to the sidebar “Distinctions Between Blame and Accountability” (see p. 4).
1. Remember that others are acting rationally from their own perspective. Given what they know, the pressures they are under, and the organizational structures that are influencing them, they are doing the best they can. Give others the benefit of the doubt.
2. Realize that you probably have a role in the situation.Your behavior may be influencing this person’s behavior and may be producing some unintended effects. Keep in mind that you will tend to justify your own actions and point of view and discount the other person’s perspective.
3. Remind yourself that judgment and criticism make it very difficult to see clearly. Judgments are mental models that limit the ability to take in new data. They tend to increase the likelihood of anger and make it difficult to learn. The following questions may help stretch your thinking and ease angry feelings. Ask yourself:
- What information am I missing that would help me understand this person’s behavior?
- How might this behavior make sense?
- What pressures is he or she under?
- What systems or structures might be influencing this behavior?
4. Use a systems thinking perspective to explore the pressures on the players involved. Notice that there are some larger forces at work that are probably having an impact on both of you. For example, when organizational goals, strategies, and values aren’t clear, groups will sometimes work toward different objectives. A group that values customer service over cost will conflict with a group that is trying to lower expenditures. Identify some key variables and their interrelationships, and ask, Is this situation an example of a vicious cycle, “Shifting the Burden,” or “Accidental Adversaries”?
5. Be willing to be held accountable. This means that, when an issue comes up, you are willing to consider whether you have lived up to your end of an agreement or expectation. Ask yourself:
- Did I have a role in this situation?
- Did I take some actions that seemed right at the time, but that had unintended consequences?
6.Work constructively with your anger. Sustained anger may point to personal issues that have been triggered by the current situation. Broken agreements, mistakes, and blame all have difficult associations for most people. However, in a learning environment, constructive resolution of conflict can also lead to significant personal growth. The guiding questions here are:
- What am I learning about myself in this situation?
- What does this remind me of?
- What new behaviors or thoughts does this situation call for that may be a stretch for me?
Interpersonal Level
Initial Contracting. At the beginning of any working relationship, it’s vital to come to some basic agreements defining the nature and scope of the work, specific and yet-to-be-defined tasks, deadlines and related outcomes, processes or methods to be used, interim checkpoints and expectations at those checkpoints, standards, and roles.
It’s also helpful to discuss what to do in the event of a misunderstanding, a lapse in communication, or a failure to keep an agreement. Imagine possible breakdowns and design a process for handling them. If breakdowns do occur, be prepared to remind others of the plan you had prepared.
When lapses do take place, they need to be brought to the collective attention as soon as possible. Misunderstandings and broken agreements often promote anger, frustration, and blame. Allowing unaddressed misunderstandings to fester can hamper productive conversations. By contrast, raising issues early can minimize escalation of problems.
The Addiction to Blame
Accountability Conversations. Once any project or working relationship is under way, it’s useful to check in periodically on the state of the partnership through accountability conversations. You may or may not have clear recollections of the initial contract regarding the task, roles, standards, processes, and expected results. Either way, it’s productive to establish or reestablish these agreements and explore what is working or not working as you take action together to create envisioned results.
Accountability conversations aren’t always easy. However, the skills they require can be applied and developed over time. Some of the basic tools of learning organizations come into play here-the ladder of inference, for example, can be used to create a conversation of inquiry rather than inquisition. The accountability conversation is also the perfect setting for practicing left-hand column skills to surface assumptions blocking honest and productive discourse. In addition, admitting the tendency to
Distinctions between blame and accountability
Here are steps for initiating an accountability conversation:
1. Find out whether the person you are working with is interested in seeing problems as learning opportunities. If so, when a problem occurs, include other people who are also interested in the situation. Other people’s perspectives can be helpful because often two people in conflict are actually mirroring the conflict of a larger system within the organization.
2. Create a setting that is conducive to learning.
- Allow plenty of time to address the issues.
- Reaffirm with each other that the goal is to learn, not blame.
- Establish confidentiality.
- Be truly open-minded.
- Listen hard to the other person’s perspective
3. Have a conversation in which the two (or more) of you
- Clarify your intention for the meeting.
- Identify the data and any assumptions or conclusions you have drawn based on that data.
- Identify the pressures each of you is experiencing in the situation.
- Identify any stated or unstated expectations. If implicit agreements were not jointly understood, this is a good time to clarify and reestablish shared agreements.
- Analyze the problem from a systems perspective. Clarify how your mutual beliefs and actions might be related and are perhaps reinforcing each other.
- Identify some new ways to address the problem.
Group Level
How people talk about one another in an organization affects the levels of accountability and trust. Often, because people are reluctant to discuss accountability issues directly, they go to a third party to relieve their discomfort and get support for their point of view. The complaint does not get resolved this way, however, although the person with the complaint gains some relief. Bringing a complaint to a third party to clarify a situation can be a much more productive alternative.
To see how this works, let’s take a situation where Tony is angry with Lee because Lee wasn’t fully supportive in a meeting. Tony complains to Robin that Lee is unreliable. Robin sympathizes with Tony and agrees that Lee is unreliable. Tony and Robin now feel closer because they share this point of view. Lee does not yet know that Tony has a complaint. Later, though, Robin, busy with other projects, puts off one of Tony’s requests. Now Tony complains about Robin to Lee, and Robin doesn’t get the necessary feedback. Over time, all of these relationships will erode.
What is the alternative to this kind of dysfunctional blaming and resentment? The solution is a deep commitment on the part of all these people to work through their reluctance to give and receive difficult feedback. In addition, they need to learn how to hold one another accountable in an ongoing way. Now, when Tony is angry with Lee and goes to Robin, the purpose is to get coaching on how to raise the issue with Lee, not to get Robin’s agreement on what is wrong with Lee. In addition, Robin’s role is to make sure that Tony follows through on raising the concern directly with Lee.
To resolve conflict directly:
1.Bring your complaints about someone else to a third person to get coaching on how to raise your concerns.
Valuable questions from the coach include:
- Tell me about the situation.
- What results do you want?
- What’s another way of explaining the other person’s actions?
- How might the other person describe the situation?
- What was your role in creating the situation?
- What requests or complaints do you need to bring to the other person?
- How will you state them in order to get the results you want?
- What do you think your learning is in this situation?
2. Raise your concerns directly with the other person. Reaffirm your commitment to maintaining a good working relationship and find a way to express your fundamental respect for the person. The ladder of inference can be a helpful tool for focusing on the problem. Start by identifying the data that is the source of your concern. Then spell out the assumptions you made as you observed the data and any feelings you have about the situation. Finally, articulate your requests for change. During the conversation, remind the other person that reviewing the concern is part of learning to work together better
3. Let the coach know what happened.
4. Outside of this framework, refrain from making negative comments about people
5. For listeners who frequently hear complaints about a third party and want to create a learning setting, it can be helpful to say something like: “I’d like to help, but only if you want to create a constructive situation. We can explore these questions; otherwise, I prefer not to listen to your complaints.”
Organizational Accountability: The IS Story
Systems thinking provides useful tools for surfacing and breaking reinforcing cycles of blame within an organization. In the story below, a group was able to use causal loop diagrams to help them move beyond blame and craft a constructive, long-term solution.
The Information Systems group of a manufacturing plant was meeting to discuss their lack of progress on a large project to overhaul the department. Initially, the IS group decided that top management’s actions caused the group’s ineffectiveness. The plant management team (PMT) kept adding projects to the group’s already full plate. Members of the PMT responded to “squeaky wheels” by giving otherwise low-priority projects the force of their support. Also, the PMT didn’t reinforce plant wide policies the IS group had developed. Most important, the team didn’t give group members the support they needed to stick to the IS overhaul they had committed to, and wouldn’t give them the budget to hire the additional staff they sorely needed.
But when the group mapped out their current situation in a causal loop diagram, they gained a new perspective on the problem. They found that the situation resembled a “Success to the Successful” story, in which two or more projects or groups compete for limited resources.
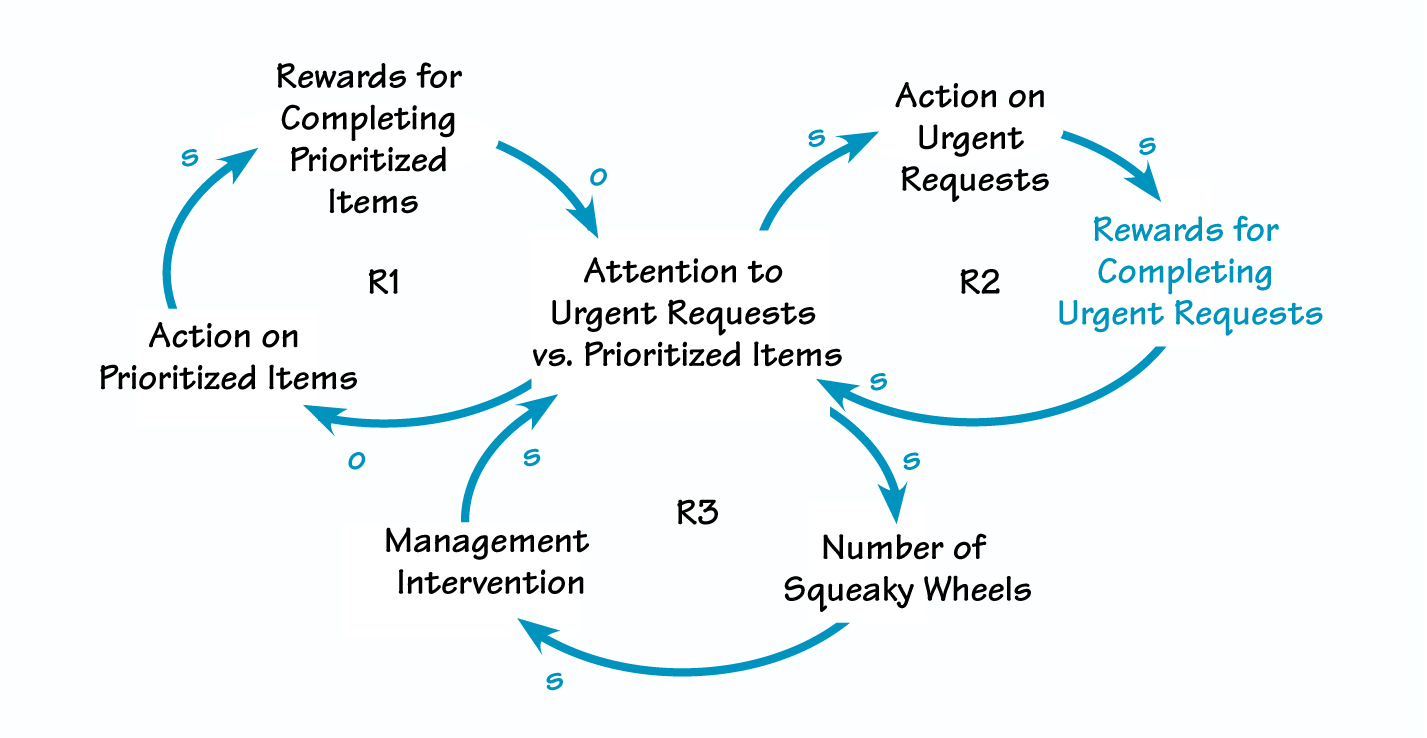
The diagram “Success to the Squeaky Wheel” shows how, in this case, the IS group’s attention to urgent requests diverted resources away from prioritized items. Because rewards for completing urgent requests were heightened, the urgent tasks continued to receive greater attention (R2). At the same time, the rewards for and focus on prioritized tasks decreased (R1). Finally, as people realized that urgent requests received greater attention than prioritized items, the number of “squeaky wheels”-or people promoting their own agenda items to management-proliferated. This development was followed by an increase in management’s efforts to get action on those agenda items, which further promoted urgent items over prioritized ones (R3).
After examining the causal loop diagrams, the group realized that they had played a role in the stalled progress on the overhaul project. Although IS team members encouraged each other to blame the PMT, no one in the group had given the PMT feedback concerning the impact of their requests and lack of support.
Success to the squeaky wheel
Armed with a systems view, the group identified several actions they could take to shift these unproductive dynamics. They decided to tell the PMT that they recognized that the IS overhaul was a top priority for the plant as a whole. They would point out that they couldn’t make progress on the overhaul if they continued to respond to “squeaky wheels. “The group would also let the PMT know that when they received additional requests, they would ask:
- How much of a priority is this request for you?
- Are you aware that there is a tradeoff in priorities?
The group concluded that they would issue a memo to the PMT describing their priorities and soliciting the PMT’s support of those priorities. They would also request that the PMT clearly communicate the priorities to the rest of the plant. In the memo, they would indicate the tradeoffs they were making and identify how their choices would help the company as a whole. The group felt that, with the PMT’s support, they would have the authority to focus on the prioritized project instead of responding to urgent requests.
Conclusion
Developing accountability skills is challenging; it takes courage and the willingness to learn new ways of thinking and acting. So why is moving from blame to accountability worthwhile? Because blame is like sugar – it produces a brief boost and then a let-down. It doesn’t serve the system’s long-term needs and can actually prevent it from functioning effectively. On the other hand, developing accountability skills and habits on every level of your organization can be an important element in maintaining your organization’s long-term health.
Marilyn Paul, PhD, is an independent organizational consultant affiliated with Innovation Associates, an Arthur D. Little company. She has sixteen years of experience facilitating organizational change. One focus of her work is peer mentoring and capacity development.
