Innovative approaches to solving large societal problems are producing some impressive results. Banks are teaming up with community groups to find ways to generate profits and support local economic development; construction companies are working with nongovernmental organizations to produce income and develop sustainable water and sanitation systems for the developing world; environmental activists and corporations are partnering to improve competitive positions and preserve the environment.
When formalized into new patterns of working together often through the creation of new umbrella
THE THREE SECTORS
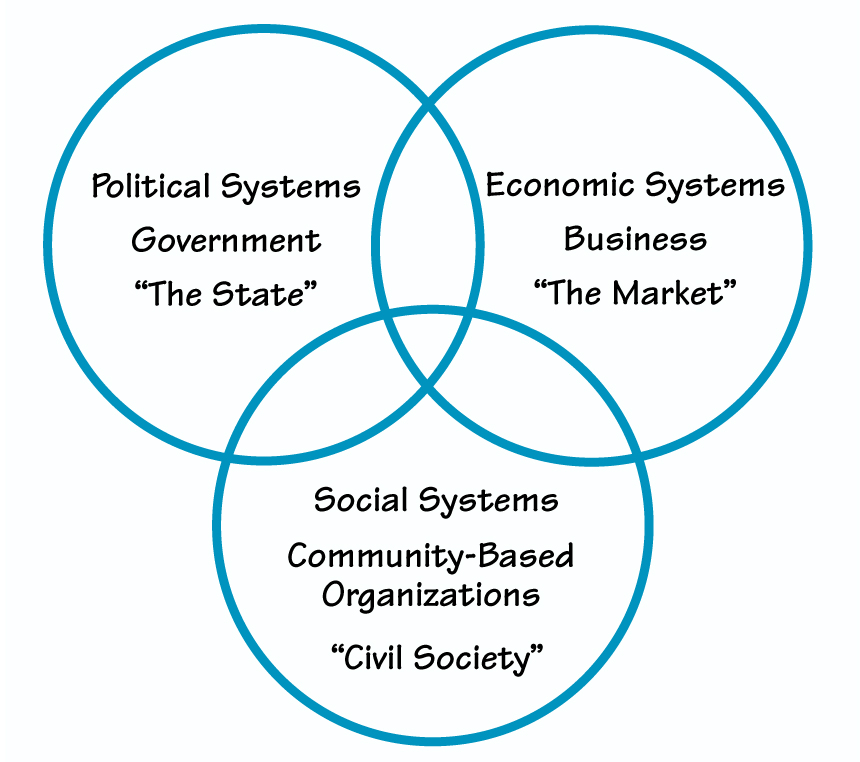
organizations with participants from diverse parts of society these mutually beneficial outcomes represent societal learning. Societal learning is a process of changing patterns of inter actions within and between diverse organizations and social units to enhance society’s capacity to innovate. Large scale problems such as poverty and environmental degradation require substantial societal learning in order for lasting change to occur.
Societal learning almost always involves the collaboration of the three organizational “sectors”: government, business, and civil society organizations (labor, community-based, religious, and nongovernmental entities). These sectors represent the three key systems of our society: political (government), economic(business), and social (civil society) (see “The Three Sectors”). All organizations can be categorized as being in one of the three organizational sectors, or as a hybrid of them. Any business that wants to profoundly alter its operating environment, any government that seeks to undertake fundamental reform, and any people who want to improve the world must partner with others from outside their sector.
Although societal learning represents an enormous challenge, the good news is that we have learned a lot about this process, and we have increased our capacity to make it happen. Still, the concept of undertaking big systems change is just beginning to influence the ways in which organizations operate.
Challenges of Societal Learning
Although related to individual, group, and organizational learning, societal learning is particularly challenging to achieve. Why? First, it necessarily involves changes in how complex institutions from different sectors operate, both separately and in tandem. So, for instance, in partnerships among environmentalists, government agencies, and corporations, all parties must embrace diverse view-points, forge new visions, and be willing to operate differently in the future than they have in the past. Reaching this level of cooperation and accommodation takes much work and a high degree of commitment, but the goal in this case, enhancing environmental sustainability is deemed well worth the effort.
Often, organizations discover that they must redefine the business they are in. In developing countries, many construction companies no longer regard themselves merely as builders of physical infrastructure, but rather as part of a joint effort to create sustainable water systems. This shift in perspective has enormous implications for how these businesses organize and undertake work. For instance, in order to engage the local communities in planning and building the infrastructure, they must take a broader approach to achieving their goals than simply completing project milestones on a tightly managed timetable.
Second, this kind of learning can take place on a local or regional level, but it also happens with global scale projects. For example, the Youth Employment Summit (YES) is a nongovernmental organization (NGO) that seeks to generate 500 million new employment opportunities for youth around the world over the next 10 years. This work involves generating cultural change through the interaction of businesses, governmental agencies, nonprofits, and others to boost the position of youth in society. An effort of this scope requires tremendous resources human, financial, and so on and profound levels of learning to accomplish.
Dynamics of Societal Learning
Given their ambitious goals, societal learning initiatives must go well beyond simply coordinating organizations and resources often referred to as single loop learning or first order change because it occurs within current structures and assumptions. Societal learning requires a shift in mental models and the development of new structures and processes, known as double loop learning or second order change.
Like organizational learning, societal learning deals with exploring the deep, underlying structures that drive behavior, surfacing the basic assumptions
BANKING ON COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT
In the 1960s, some U. S. banks began to flee the inner cities as the racial and economic complexion of those areas changed. These banks followed their traditional middle class white clients to the suburbs. This shift resulted in substantial “disinvestment” in cities, as financial institutions refused to grant mortgages and loans to the people who lived there, often while continuing to accept their deposits.
The banks viewed their actions as the privilege of private organizations and refused to talk with community based organizations (CBOs) about disinvestment concerns. CBOs had difficulty articulating their argument or even measuring the problem because of lack of access to bank lending data. In response to community protests, state and federal governments passed legislation that obliged banks to talk with their communities and give CBOs access to their data about loans and deposits.
As a result of the legislation, banks and CBOs have negotiated ways to increase banks’ products and markets in profitable ways to include the inner cities. This process involved a shift in assumptions by both parties and an array of new organizations and people specializing in making the connections work through new products, delivery vehicles, and capacity. A positive outcome of this process was that a 1999 merger proposal between Boston banks included a provision for $14.6 billion in loans to local communities over five years.
Some banks have discovered that they have developed a valuable capacity through this process that they can apply elsewhere. For example, Citibank has built its retail presence in India in part through community banking like approaches. Given that Indian banks focus almost entirely on the upper income market and have essentially no experience serving lower income areas, Citibank has a clear advantage and a sound strategy for entering the Indian financial services market.
we hold that limit our options, and developing innovative approaches to persistent problems. For instance, throughout the U. S., intense interaction between the banking industry and community based organizations (CBOs) revealed that the bankers’ view of poor neighborhoods as unprofitable markets was grounded not just in social biases but in fundamental business assumptions (see “Banking on Community Development”). Through their discussions with community representatives, the bankers began to understand that their assumptions about the poor were wrong. They also found that their rigid ideas about their own product lines, product development approaches, and delivery systems were the real limiting factors to the success of banking services in the neighborhoods, not the limited resources of the people who lived there. Working with CBOs and churches, the banks revamped their business models in order to better serve and profit from the community. Making this change happen took the creative synergy of all parties involved.
This kind of shift in thinking can spur complex synergies and powerful innovations. For example, the banks found that they needed to design new product development tools, because traditional telephone surveys and focus group methodologies were inadequate for conducting market research with individuals who don’t have strong English-language skills. The CBOs thus became expert articulators of their constituents’ needs and worked with the banks to develop, deliver, and manage leading edge products. Similarly, in South Africa, organizations engaged in constructing sustainable water systems discovered that the government’s budgeting process was a barrier. Once government leaders became aware of the problem, they changed the process, leading to a whole range of opportunities.
Such collaborations can even produce the more rarefied triple loop learning, which involves rethinking the way we actually think about an issue. Through their work on change initiatives, many poor people and wealthy people, business people and bureaucrats, social activists and conservatives have come to fundamentally change how they regard one another. By coming together in productive new ways, these groups create rich networks of social capital that allow societies to accomplish things they could not have done before.
Systemwide Change
In systems thinking terms, the challenge of those involved in societal learning is to understand and address numerous large and complex feedback loops. In development and change management terms, the challenge is to transform learning at a project and intellectual level into broad, sustainable systemwide change.
Because successful societal learning initiatives usually require innovations in business, government, and civil society simultaneously, some change agents are intentionally fostering organizational networks called intersectoral collaborations (ISCs). These collaborations can form at the community level, as with many community development initiatives; at the state level, as with education and workforce development programs; and at the international level, as with the worldwide “clusters” in natural resources, water and sanitation, youth, and traffic safety initiated by the World Bank.
Such collaborations facilitate interactions among organizations from each of the three sectors in an effort to generate and apply new knowledge. Collaborating involves recasting roles, responsibilities, and allocation of benefits from the partnership. The key outcome of the process is new relationships among the three systems that lead to improved results for the organizations involved and for society as a whole.
ISCs are potent social change vehicles because:
- They bring together perspectives from each of the three key sectors of society.
- They strive to develop actions that produce value for each of the different sectors.
- They offer a broad reaching mechanism for disseminating learnings and gaining adoption of new approaches throughout society. So, rather than having a government representative urge businesses to change how they operate, business people use their own business networks to champion change, based on business experience, in a language that other business people understand.
- They provide tremendous opportunity for mobilizing the diversity and scale of resources necessary for bringing about the desired change. Business comes with its financial and production assets, government with its rule making and tax resource assets, and civil society with its foundation funding and volunteer workforce.
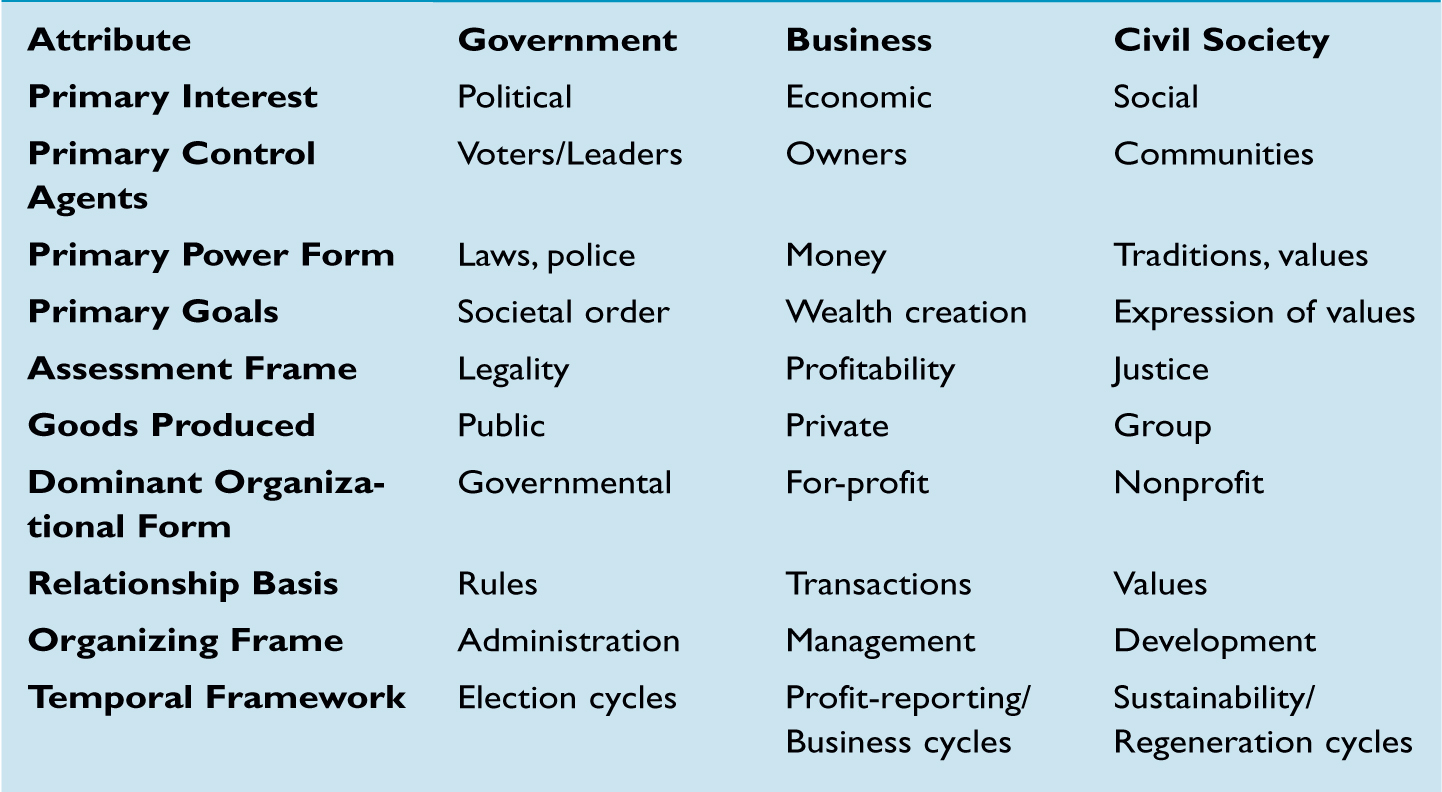
To fully appreciate the distinctive qualities that the collaborating organizations have to offer, we must understand the generic differences among the three sectors (see “Attributes of the Different Sectors”). For instance, the “Assessment Frame” refers to how members of a sector decide whether or not their output is “good.” Government is particularly concerned with legality; business focuses on profitability; and civil society thinks in terms of equity and justice. Therefore, to be successful, a societal change initiative must produce these three outcomes.
In addition, understanding the core competencies of partner organizations helps participants better define their own roles in learning initiatives. This process emphasizes the rationale for bringing organizations in different sectors together in the first place: to combine core strengths and offset weaknesses. An entity in one sector may be less able to accomplish a certain task than an organization in another sector. For instance, a business may be proud of customers’ trust in its products, but it is impossible to compare consumer confidence to the level of trust that a good civil society organization, such as a church, can build within its community.
Civil society organizations tend to define their issues as “problems,” whereas businesses like to frame them as “opportunities.” YES originally defined its goals from a problem and social justice perspective young people lack jobs. Through their work with business partners, organizers came to understand that failing to articulate the business benefits of their mission might ultimately limit its appeal. YES was then able to identify a number of positive business outcomes, ranging from market development opportunities to support for human resources planning, that their program might produce.
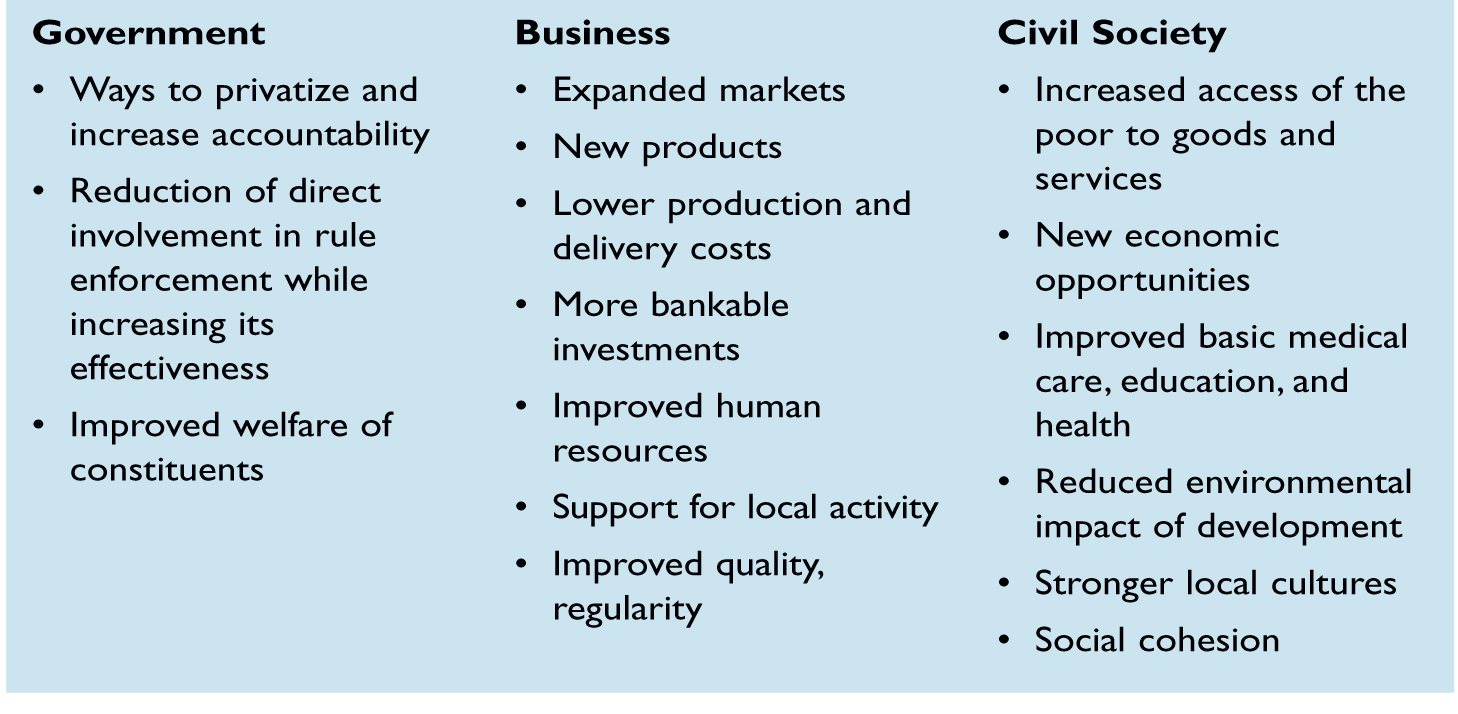
Through productive debate and dialogue among the diverse participants, ISCs can maximize the contributions of each sector and produce innovations that are valuable for all involved (see “Potential Outcomes by Sector” on p. 4). These innovations typically could not be thought of or implemented by the participants on their own. For this reason, to be successful, collaborators must be willingly to share their own goals and processes openly.
For example, environmentalists have been able to point to creative ways in which businesses can significantly
ATTRIBUTES OF THE DIFFERENT SECTORS
reduce their energy costs; similarly, interaction with consumer advocates has led some companies to move from merely complying with government regulations to creating new products and markets by anticipating changing consumer desires and the resulting legislation. Thus, it is important to understand the distinct goals of organization members and build mutual commitment to achieving them. Partners must also be able to define collective goals part of a shared vision.
Developing a Societal Learning Initiative
Developing a societal learning initiative requires patience, vision, and commitment. These transformations take time. About two decades passed before substantial changes occurred in the banking industry in inner cities in the U. S. However, as knowledge about how to collaborate on complex ventures grows, we’re considerably reducing the length of time it takes to realize successful outcomes. Depending on the scale and complexity of the task at hand, some initiatives can achieve significant results within three to five years.
Sometimes the collaborations begin as an NGO program, sometimes out of an event that produces common recognition that a problem/opportunity requires the resources of diverse organizations, and sometimes under the leadership of an influential individual or organization, such as a government agency. Often associations and federations of organizations take the lead in these initiatives, because such entities represent a large number of constituents faced with the same problem. However, societal learning efforts must also include frontline organizations, such as individual businesses, because these participants have different knowledge and concerns than do the associations that represent them and their industry partners and competitors.
Because these largescale projects are at the leading edge of what we know how to do in terms of creating change, they require ongoing learning and the development of innovative processes and structures. Organizers of societal learning ventures should keep the following principles in mind:
POTENTIAL OUTCOMES BY SECTOR
1. Make learning the guiding framework. Adopting a learning framework means that leaders must incorporate a planning action reflection cycle into every aspect and stage of the project. To do so, all participants need to agree that initial plans will be intentionally broad and that details will develop as the project proceeds. In the case of the World Bank clusters mentioned above, participating organizations began with a relatively vague idea about what they might do together. After getting to know one another, they developed learning agendas that included both looking at current strategies for working together and under taking experiments with new joint activities. A disciplined process to engaging participants in gathering data and analyzing it in real time is also a key way to develop common understanding about new ways to work together more effectively In addition, adopting a learning framework means providing workshops and other opportunities for skill development, because changing systems requires that we also change individual behaviors including our own. For example, the concept of, “co-leaders” is a natural extension of the need for peer like relationships among sectoral organizations. Rather than having “one captain of the ship,” several people share leadership. Currently, few people have the skills and few organizations have the structures and processes to share leadership responsibilities. We need to develop these abilities to move ahead with significant social change efforts.
2. Use action learning to support the societal learning process. Action learning involves developing knowledge about how to approach an issue and then creating a strategy for doing so, while at the same time gathering data to refine the approach. Coupled with systems thinking skills, this methodology can help people simplify and clarify complex problems. The World Resources Institute is using this technique to develop management tools to help governments, NGOs, and companies fulfill commitments made in international environmental conventions.
3. Begin by thinking through the full spectrum of issues involved in addressing a challenge. Governments and development agencies have long thrown money at the problem of inadequate water services in the developing world. Time and again, they have organized government bureaucracies or hired international engineering firms to build infrastructures of pipes, dams, and water treatment plants. Within six months, the new infrastructure is often in disrepair, and people are getting water through their traditional methods. Now that’s a fix that fails!
In this example, the well-intentioned parties wrongly define the problem as strictly a technological one, rather than also being one of societal learning. Analyzing the current situation and the intended outcome would define not just the necessary physical infrastructure, but also the changes in behavior, beliefs, resources, and organizational support required to optimize outcomes. The analysis should also show critical barriers to success; for instance, many people in the developing world think of water as being free and are unwilling to pay for it; communities cannot afford to remain dependent on outside experts to operate and maintain the system; and communities need to have a regulatory structure to monitor the system and ensure that it functions to quality standards.
4. Map the current system. Participants should take the time to identify all stakeholders in the system and analyze the relationships among them. Doing so offers planners a sense of the current reality, the key stakeholders, and the actors involved. It can also help them to identify organizations that are “early movers” an important category in any change process, because they are the ones most likely to lead the effort.
5. Follow the traditional planning action reflection learning process. Convene the players to investigate possible new directions; collectively design pilot projects and implementation steps; define learnings; plan for scaling up the initiative; scale up implementation, and so on. One important task is to develop tools to address classic problems that frequently crop up, such as maintaining the commitment of organizational participants; addressing “glocal” (global local) concerns (ensuring that the venture responds both to local needs and those of outside participants); maintaining organizational simplicity in the face of task complexity; and producing valuable outputs for both the overall project and the individual organizations. Regular review processes are part of the important work of formalizing feedback loops.
Unintended Consequences
Given the large number of variables in such global efforts, there are often many unintended consequences. In the banking example, some CBOs found that their increasingly close ties to the industry undermined their support from within their communities. Construction companies in developing countries realized they had to rethink their business model. And by decentralizing and privatizing public services, governments often discover that they need new budgeting, monitoring, and regulatory processes. All of these lessons reflect deepening societal learning. When the collaborations are working well, these lessons will be ongoing and profound.
As with any innovation, societal learning can involve substantial conflict. In successful collaborations, dynamic tension does not go away, but the parties find ways to harness that tension. Sometimes, the disappearance of tension indicates that societal learning is not occurring that collaborators are having difficulty getting beyond the exchange of pleasantries to get to the hard work of grappling with deeper issues and differences. Or, the lack of conflict might indicate that societal learning has already occurred, and the collaboration is moving into a maintenance stage. The absence of tensions usually indicates that participants should reassess the purpose of the collaboration, whether it has resulted in societal change, whether the change is limited to a small group of organizations, whether external change has made the collaboration irrelevant, or whether there is a new purpose that the group wants to develop.
Enormous Potential
Organizations often approach today’s problems and opportunities from yesterday’s perspective. Nevertheless, much has changed in the last decade. In that time, many new NGOs and businesses have formed; even more important, there are now improved global networks including the World Business Council for Sustainable Development, the International Business Leaders Forum, and CIVICUS (a civil society organization) that are engaged in intersectoral collaborations. Through experiments with these collaborations over more than a decade, we have vastly improved our knowledge about how to develop and sustain them. In this way, we have substantially increased our capacity for societal learning and our ability to effectively address complex issues such as the environment, war, and poverty and to create outcomes that are win win for all segments of society.
NEXT STEPS
Is a Societal Learning Approach Appropriate for You?
Societal learning strategies are complex and demand an initial commitment of three to five years before they really start to produce valued outcomes. Therefore, any organization considering initiating or joining such a venture should consider the following key questions:
- Does effectively addressing the problem/opportunity require participation of stakeholders from different sectors?
- Is there a convener who can bring the parties to the table?
- Do the stakeholders perceive that an ISC-societal learning approach might address an issue better than other strategies?
- Are resources available to support initiation?
- Are key stakeholders willing to explore opportunities together?
- Is the potential benefit from an ISC-societal learning approach worth the cost?
