Trust is a subject close to many people’s hearts. Whenever I make presentations on this subject, I never cease to be amazed by the number of people who approach me afterward to share examples of the importance of trust in their lives. What I have discovered during the course of these conversations is that most of us have a deeply rooted desire to live and work in environments in which trusting relationships and trustworthy behaviors are the norm rather than the exception.
I have also observed that the amount of trust that exists within a group of people greatly affects the results they can achieve together. A guest on a recent talk-radio show on financial investments demonstrated the impact of trust within the U. S. economy. A highly respected portfolio manager with 40 years of success in mutual fund investing, he remarked that, despite Alan Greenspan’s testimony before Congress that the economy is moving in a positive direction, the stock market is still slumping. Historically after recessions, markets recover first, followed by the rest of the economy; yet in our current situation, the economy is showing signs of recovery but the markets are still experiencing downward trends. Why? The guest attributed the slow market improvement to human factors. He asserted that, in response to gross misrepresentation of earnings and other mismanagement by top executives from companies such as Enron and Worldcom, many people now distrust large corporations and hesitate to invest in them. In other words, despite signs that our economy is getting back on track, trust — or lack of trust, in this case — appears to be significantly limiting the recovery of the markets and the economy as a whole.
THE ICEBERG MODEL OF TRUST
As a result of my observations and conversations with others about this topic, I have been investigating how to build trust in organizations, particularly schools. I’ve looked at numerous studies that have attempted to define trust and explain how it works. While thought provoking, their findings leave me unsatisfied. One of the reasons I am not adequately convinced by many researchers arguments is that their approach to understanding trust tends to be deconstructivist.
They break apart the concept into many different components in order to analyze it, and the more they do, the less I understand and connect with it.
I have come to believe that we can better understand trust by looking at it as a system composed of many independent yet interrelated and interconnected factors, including but not limited to integrity, honesty, character, reliability, and competence. Because the power of trust lies in the synergy of these variables, building it requires us to understand their interplay in our relationships and in our organizations.
In a recent article, Peter Senge touched more deeply on this process when he discussed the importance of “holism,” a way of understanding the world whereby “the whole is enfolded into each element or part” (see “Creating the World Anew,” The Systems Thinker, V13N3). It is a way of seeing not only the interconnections among the parts and the whole, but also how they mutually evolve together. I believe trust is a concept to which holism applies: We cannot adequately understand and nurture its components without looking at the essence of the whole concept. In our attempts to break it into what appears to be its constituent parts, the “spirit” of trust no longer exists.
To illustrate, let’s try to isolate one of trust’s components, honesty. Although honesty is a positive trait for which we should strive, an honest person is not necessarily reliable or dependable, two other components of trust. Would we trust an honest but unreliable person? We might have confidence that that person will tell the truth, but we probably wouldn’t trust him or her to follow through with commitments. As Stephen Covey puts it, would we really trust an honest but incompetent surgeon to perform a major operation on us? This example hints at the complex nature of this seemingly simple characteristic.
Defining Trust
Let’s begin by defining trust. Webster’s Dictionary says trust is “firm reliance on the integrity, ability, or character of a person or thing” and “assured resting of the mind on the integrity, veracity, justice, friendship, or other sound principle of another person.” Stephen Covey defines it as “the balance between character and competence.” These definitions focus on a particular state of mind that one needs to be able to trust someone.
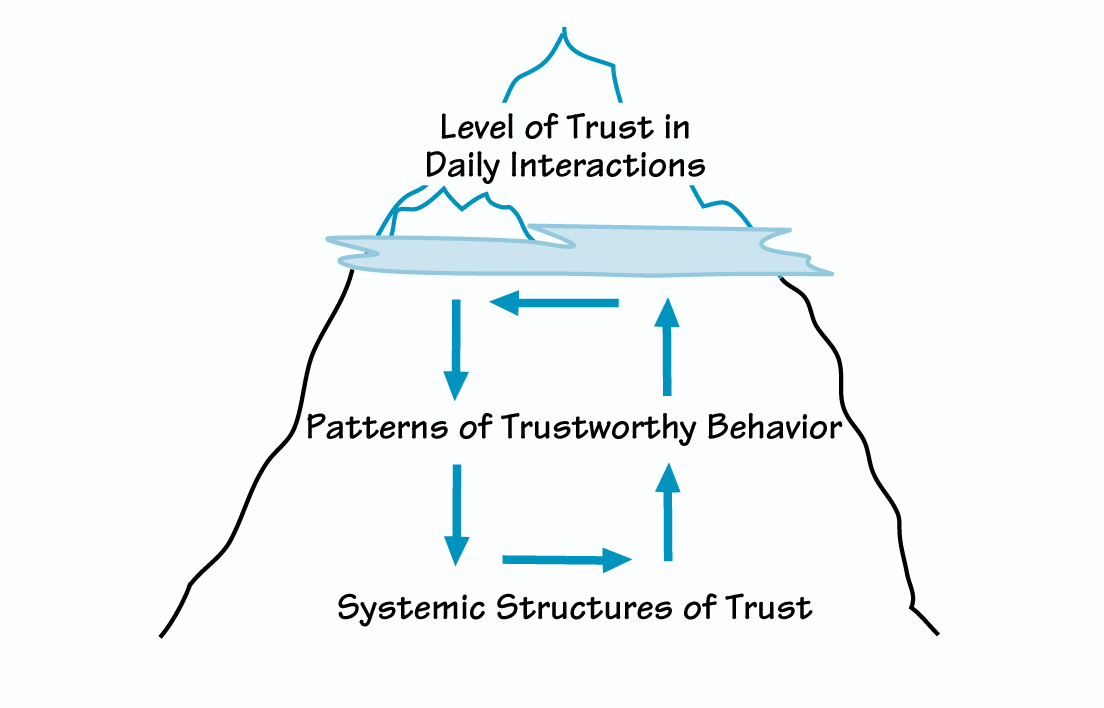
But if instead we think of trust as an underlying condition necessary to support all effective human interactions, then it becomes a foundational systemic structure. In this supporting role, trust is not visible in the traditional sense; like the wind, only its effects can be seen. For example, trust is absent if we think a relationship might jeopardize our personal or professional interests and well-being. Similarly, we can comfortably surmise that high levels of trust exist in organizations in which members feel a sense of community and connectedness.
To explore the idea of trust as an actual but intangible structure, let’s consider the iceberg metaphor. When you look at an iceberg, only the tip is visible; the greater mass lies out of sight below the surface. By looking “beneath the surface” of daily events in your organization, you can determine the structures that influence people’s behavior. If we apply this metaphor to understanding trust, the tip is our daily interactions in which we experience varying levels of trust or mistrust (see “The Iceberg Model of Trust” on p. 2). These interactions, a series of seemingly unrelated events, are the concrete results of an organization’s climate of trust, which exists in the patterns and structures “below the waterline.” One unpleasant encounter may not lead us to feel an overall sense of mistrust. But if the behavior continues over time, it’s likely to undermine relationships and erode trust throughout the organization. (Note that certain events, such as layoffs, are significant enough to be “trust busters” the first time they occur.)
Using the Trust Lens
So how do we notice patterns of behavior that support or undermine trust? By looking through a “trust lens.” In almost every interaction between people, a “trust transaction” takes place that transcends the actual event; that is, based on what occurs, levels of trust rise or fall. To determine the degree of trust being transacted during an interaction, you can take the following elements into consideration:
- The history of interactions between individuals and/or groups (What has happened between them in the past?)
- The literal meaning conveyed through the interaction (What words are being expressed?)
- The inferential meaning conveyed through the interaction (What voice tones, facial expressions, and body language are being used?)
- The result of the interaction (Did one party gain an advantage over or “hurt” the other in some manner?)
If we think of trust as an underlying condition necessary to support all effective human interactions, then it becomes a foundational systemic structure.
Knowing the history between two parties offers us the greatest insight in determining the level of trust transacted in a given encounter. Consider, for instance, how different your conclusions would be if you knew that two individuals you were observing had been best friends their entire lives or that two groups had previously experienced a significant conflict with each other.
Because we don’t always know the history, we can try to “read” the trust transaction at both the literal and inferential levels. At the literal level, we analyze the words and phrases being transmitted between the parties involved. In general, using deceptive, demeaning, and intimidating language diminishes trust, while communicating openly and honestly with what Covey calls “courage and consideration” builds it.
Observing literal transactions has its limits, though. According to numerous studies, the words we use make up only about 10 percent of what we communicate. It is at the inferential level — the voice tone, facial expression, and body language — where we do 90 percent of our communicating. Psychologist Gwyneth Doherty-Sneddon says that “language is seen as the primary vehicle” to transmit information and “non-verbal communication is primarily seen to transmit emotional information.” Thus, actively observing all aspects of an interaction and asking, “Do these behaviors convey trust or lack of trust?” is crucial in determining the degree of trust being transacted.
We have to be cautious, though, whenever we try to determine levels of trust, because we each bring to any situation our own set of assumptions about how the world works. Therefore, when we use a “trust lens,” we need to consider how our mental models are influencing our perceptions. A continual comparison between actual data and our assumptions will help us to discern whether we are making accurate judgments or whether we are overgeneralizing based on limited information.
How Trust Becomes a Structure
When a pattern of transactions occurs over a period of time, it creates a structure that becomes the “cultural norm”—a climate of trust or mistrust. In a reinforcing process, our behaviors strengthen the cultural norm, which strengthens the behaviors, and so on. For example, suppose a number of people in an organization behave dishonestly — perhaps by misrepresenting financial data — to help the organization “get ahead.” If the organization’s leaders fail to censure the dishonest conduct, the organization will assume that “this is how we do business.” In this way, isolated behaviors grow into a pattern of dishonesty. Likewise, when trustworthy behaviors, such as honest communication, competence, and integrity, are modeled and reinforced, they eventually become the cultural norm.
Another example is using standardized testing as the sole mechanism for assessing the quality of a school system, which may end up creating a culture steeped in cynicism and deceit. In order to maintain their school’s stature in the community and — in some cases, even it’s funding — some teachers might end up “teaching to the test,” basing their lesson plans on the test questions rather than on sound curriculum. And, in extreme cases, this emphasis on “making the grade” might even influence students to cheat, especially if passing the test is the only way to advance to the next grade or graduate.
The scenario seems like a “chicken and egg” syndrome: Did the structure cause the behaviors, or did the behaviors create the structure? I believe the answer is “yes” to both questions. We may blame lack of trust on the “system,” but we need to remember that, with or without intention, we create and reinforce that system through our behaviors.
LOW TRUST IN AN ORGANIZATION
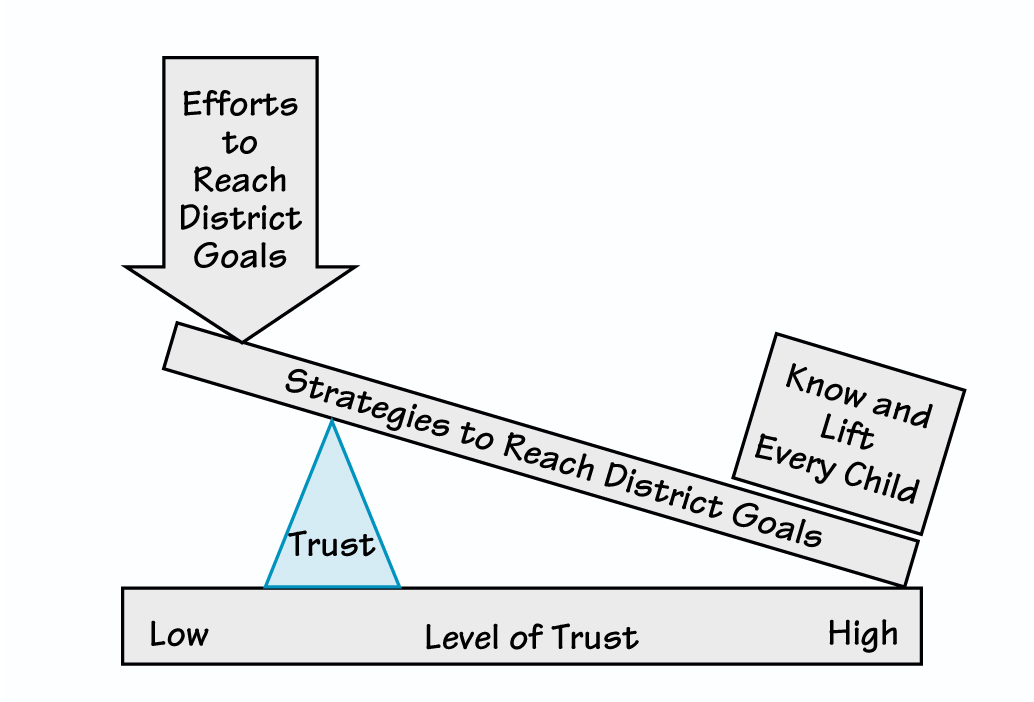
If the lever is a district’s strategies for reaching its objective — helping every child reach his or her potential — then the position of the fulcrum reflects the level of trust within the organization. In a low-trust environment, the fulcrum is far away from the goal. People end up expending more effort to achieve the objective than they might otherwise in a high-trust environment.
In this sense, we might view trust as an example of what system dynamicists call “dynamic complexity,” because the effects of trustworthy or untrustworthy behaviors in an organization are not always closely related in time or space to when they actually happen. In fact, the impact is often felt much later. So to nurture trust, we need to practice the art of simultaneously “seeing the forest and the trees” — seeing the organizational culture and the individual behaviors within it.
Leveraging Trust
Activities such as mandated standardized testing, which attempt to solve a complex problem in one fell swoop, reflect the prevailing system of management in most organizations today. In a keynote address at the Systems Thinking and Dynamic Modeling Conference in June 2002, Peter Senge described the attributes of this type of organization:
- Culture of compliance
- Management by measurement
- Right and wrong answers
- Managing outcomes versus designing systems
- Uniformity
- Predictability and controllability
- Excessive competitiveness
- Loss of the whole (person, connections to others and to the world)
This management structure creates an environment that undermines trust and produces a, “Trust Death Spiral,” in which mistrust and low performance continually reinforce each other. In this setting, people may feel that they must do whatever necessary to get ahead or even survive in the organization. From a systems thinking perspective, to move away from this kind of management system and toward one that is fundamentally transformational and empowering in nature, we need to understand how an organization’s interrelationships, processes, patterns, and underlying structures influence individual and group behaviors — and how we can leverage trust to change those dynamics.
What does it mean to leverage trust? Archimedes, one of the world’s great mathematicians, claimed that he could transport the globe with a lever, saying, “Give me a place to stand on, and I will move the earth.” The principle of how a lever and fulcrum work together can help us understand how trust influences an organization’s ability to reach its goals.
A lever is a stiff beam that rotates about a point of support called a “fulcrum”; one end of the beam goes under an object to be moved. The purpose of this simple machine is to lift a heavy load using the minimum possible force. How much force you need depends on the length of the lever and where you place the fulcrum. Since it’s often not possible to change the length of the lever, to get the highest leverage, you need to focus on the position of the fulcrum. To minimize effort, place the fulcrum so that it’s close to the object and push on the other end. This is how a jack raises a car so we can change a tire. If the fulcrum is farther away from the object, you’ll need to apply greater force to the lever to lift it.
Low Trust. Let’s apply the metaphor of a lever and fulcrum to the organizational setting. If the lever is a district’s strategies for reaching its objective — helping every child reach his or her potential — then the position of the fulcrum reflects the level of trust within the organization. In a low-trust environment, the fulcrum is far away from the goal. People end up expending more effort to achieve the objective than they might otherwise in a high-trust environment. For instance, if administrators of a school district and its professional teacher organization mistrust each other, the district may spend more time settling disputes than fulfilling its true mission to educate children (see “Low Trust in an Organization” on p. 4).
High Trust. When the trust fulcrum is in a more advantageous position, most institutional actions can be directed toward fulfilling the organization’s mission. In the example above, if the school district works closely with its professional teacher organization to nurture a trusting, mutually beneficial relationship, it will likely not have to direct so much effort to managing that dynamic and can instead focus on educating children (see “High Trust in an Organization”).
Organizations that build systems and structures that nurture high trust and mutually beneficial relationships can trigger a “Trust Growth Spiral.” In this positive reinforcing process, trust and consequently high levels of performance mutually reinforce one another. Increased trust results in intangibles, such as confidence, pride, and ownership, which lay the psychological foundation for continued success, thereby inspiring even greater levels of trust.
Building Trust
In most organizations, the process of building trust consists of occasional events designed to promote teamwork. Many of us have participated in activities such as “supportive chair trust circles,” in which people simultaneously sit on the lap of the person behind them and support the person in front of them; eventually, the entire group is seated in a circle without the use of any props. In “trust falls,” one partner closes her eyes and falls backward, trusting that her partner will catch her before she hits the floor. While fun (unless your partner doesn’t catch you!), these exercises only tap the surface of what it takes to build trust in an organization.
Creating lasting trust is not a one-shot deal; it is an ongoing process that requires deep, long-term commitment from everyone involved. So how do we begin? Following are some examples of how my organization, the West Des Moines Community School District in Iowa, has sought to understand the systemic nature of trust and then work to create structures and engage in behaviors that enable it.
In 2000, the administrative staff development planning team, part of the Administrative Leadership Team (ALT), began to design a three-year leadership development program. We found that we value what the IABC Research Foundation has identified as five qualities that high-trust cultures generally acknowledge and reward:
- Competence (workers’ effectiveness)
- Openness and honesty (amount, accuracy, and sincerity of information shared)
- Concern for employees (exhibition of empathy, tolerance, and safety)
- Reliability (consistent and dependable actions)
- Identification (sharing of common goals, values, and beliefs)
To evaluate the levels of trust in our organization, the ALT disseminated a 16-question trust survey to all its members. The results revealed that, while the perceived level of trust was generally high, some items scored relatively low on the overall trust barometer. Based on those results, we initiated a four-session in-service training during the 2000-2001 school year. The sessions involved all building and district-level administrators and focused on identifying trustworthy and untrustworthy behaviors and their impact at the interpersonal and organizational levels. Feedback following each session was overwhelmingly positive. Results from a follow-up survey revealed an improvement in perceived levels of trust among ALT members.
HIGH TRUST IN AN ORGANIZATION
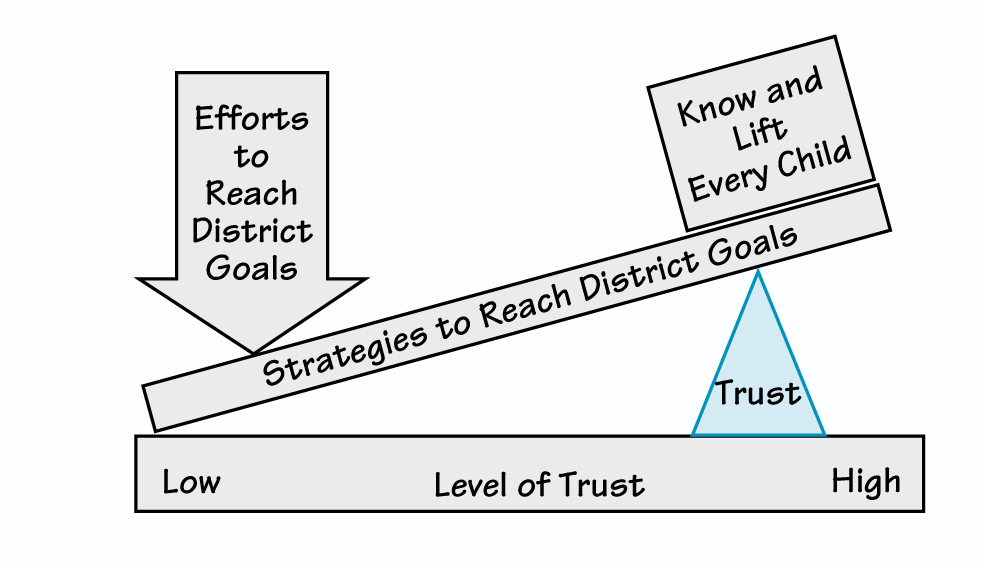
When the trust fulcrum is in an advantageous position, most institutional actions can be directed toward fulfilling the organization’s mission rather than dealing with interpersonal issues.
Here are some of the breakthroughs we have achieved through our efforts:
Building a Shared Vision. For several years, the district, with the vision and support of its superintendent, has embarked on building a learning community. One step in this process has been to develop a shared vision statement for the district through a series of collaborative processes with parents, students, staff, board of education members, and interested citizens. Through continued dialogue, the district generated a simple, yet powerful statement: “The West Des Moines Community School District will be a caring community of learners that knows and lifts every child. We will inspire joy in learning. Our schools will excel at preparing each student for his or her life journey.”
This shared vision is now guiding the district’s discussions, decisions, and future plans. It has:
- Provided the foundation for a major reorganization of the high school
- Caused the administration to seek to identify the students who do not feel “known or lifted” and to improve our services to them
- Influenced some conversations to focus on why and how we want students to experience joy in learning
- Brought forth community members who challenge the district to do better
In a nutshell, through a foundation of trust built through the development of our vision statement, avenues of communication are opening up.
Changing Our Mental Models.
In the early 1990s, the district’s school board created a policy that supports and encourages “participatory management.” This policy, which allows greater partnership and ownership in decision-making among all district stakeholders, has strongly influenced our mental models about how decisions should be made. At the event level, this policy demonstrates a belief in actively including those directly impacted by decisions in the process. Below the surface, the message is one of trust in the integrity, character, and competence of those once uninvolved, who now have a greater role in influencing policy.
Developing Personal Mastery.
The year-long trust-building workshop for members of the district’s administrative leadership team has brought trust and trustworthiness to the forefront of our consciousness and conversations. Our understanding of the gap between the current reality of our district’s trust climate and our future vision of a high-trust culture has inspired us to grow and learn as individuals and as a group.
Engaging in Team Learning.
Central office administration regularly conducts “maintenance” meetings with the leaders of our district’s professional and support organizations. These meetings provide opportunities for team learning through honest conversations. The conversations go beyond polite talk to deeper listening, engagement, and feedback. Using reflective skills has helped team members more effectively manage disagreement and resolve conflict.
Building Trust Informally.
Through the development of policies, practices, and cultural norms, an organization can make conscious efforts to build and maintain trust
In addition to formal organizational efforts to build trust, more informal interactions have also contributed to a high-trust climate. For example, recently, a confrontation between a teacher and student required an administrative response. Rather than the principal dictating how the teacher should handle the situation, the principal conducted a dialogue with the teacher based on the spirit of “knowing and lifting every child.” She helped the teacher recognize why the interaction did not align with the shared vision; turned the meeting into a learning opportunity; and indicated that she trusted the teacher to do the right thing. The teacher ultimately resolved the conflict with the student in a way that maintained a positive teacher-student relationship.
Benefits of a High-Trust Culture
When the level of trust in an organization is high, its influence is felt and observed at every level and in every aspect of its operations. High trust allows organization members to focus on their primary mission rather than taking precious time and energy to deal with the numerous crises that prevail in a low-trust environment. They can then focus their resources and energy to reach their goals.
For schools, “profit” is measured by student achievement. A multi-year study completed by University of Chicago professors Anthony S. Bryk and Barbara Schneider resulted in the book Trust in Schools: A Core Resource for Improvement (Russell Sage Foundation, 2002), which links higher student achievement with high levels of trust between teachers and principals and among the teaching staff. Bryk and Schneider go so far as to say that without trusting relationships, school improvement efforts are “doomed to fail.”
For all kinds of enterprises, trust is a high-leverage resource that sustains success and effectiveness. Through the development of policies, practices, and cultural norms, an organization can make conscious efforts to build and maintain trust. As an organization reaps the “profits” of a trusting culture, it simultaneously perpetuates, or sustains, trust as an important commodity unto itself.
Ultimately, trust involves developing and maintaining relationships. Today’s workplace requires effective, skilled, and compassionate transformational leaders — not just managers — who recognize the need for trust and who facilitate organizational change to create high-trust cultures. We can start this process by taking to heart the words of Edward Marshall, who said, “The answer to leading others to trust and high performance may be found by looking in the mirror and asking: Am I trustworthy?” Ensuring the answer to that question is “yes” may be the highest-leverage action we can take as leaders today.
Doug Stilwell has 22 years of experience in education. He is currently the principal of Crestview Elementary in the West Des Moines Community School District in Iowa. Doug is also a doctoral student in Educational Leadership at Drake University.
NEXT STEPS
- Assess the overall current levels of trust in your organization through a survey.
- Encourage open and honest communication, especially opposing views that are presented in a productive way, and then be willing to listen
- Examine policies, practices, and behavioral norms in your organization. Do any have unintended consequences that damage trust?
- Use the “trust lens” to observe interactions among people and look for behavior patterns. Reinforce behaviors that support trust and seek to eliminate those that undermine it.
