“What would be more interesting to you,” I ask an audience of executives, “engaging in a dialogue on learning how to coach or one on learning how to learn?” Generally, 80 to 90 percent of the executives vote for coaching. I point out the obvious—if you learned how to learn, you could apply the knowledge to learning anything, including coaching. And the reverse is not true. So why not learn how to learn?
The answer is usually unspoken but real. Coaching is something I do to improve another person or team; it’s part of my job. Learning happens to me; it makes me feel vulnerable. Learning focuses on my weaknesses, pressuring me to change the way I think and behave. Besides, I’m a professional, with established competencies and knowledge. I’m paid to get results, not to learn.
Thus, managers’ most common response to the growing demand for corporations to become learning organizations is to scramble to be the teacher, not the taught—the coach, not the coached. But, to be an effective coach, an individual must understand the nature of learning. And to understand learning, a coach must be actively engaged in the learning process and personally familiar with the kinds of vulnerabilities and obstacles a learner experiences.
Developing Learning Capability
Learning, coaching, and building a learning culture are critical to the success of modern businesses. Because learning increases our ability to perform, the capacity to grow capability is becoming indistinguishable from the capacity to grow wealth. However, unacknowledged resistance to learning and coaching can make it difficult for us to realize the ideals of the learning organization.
As children, we were naturally engaged in learning in everything we did. Thus, as adults, we don’t really need to learn how to learn, as much as we need to remember what we once knew. We need to unlearn some of the attitudes and practices we picked up from our formal education that seriously undermine our natural appetite and inherent capability for learning.
The Inner Game approach (see “The Inner Game™” on p. 2) is about unlearning the personal and cultural habits that interfere with our ability to learn and perform. The goal is simple, if not easy: to give ourselves and our team’s greater access to our innate abilities. The approach can be summarized in a simple formula:
Performance = Potential – Interference
“Potential” includes all of our capabilities—actualized or latent—as well as our ability to learn; “Interference” represents the ways that we undermine the fulfillment or expression of our own capacities.
Diminishing the Obstacles to Learning
We can achieve increased capacity for performance and learning either by actualizing potential or by decreasing interference—or by a combination of both. In my experience, the natural learning process—which is how we actualize potential—is gradual and ongoing. By contrast, reducing interference can have an immediate and far-reaching impact on learning and levels of performance. Thus, a successful model for skill development must take into account the phenomenon of interference.
But beware: The barriers to learning are often well guarded and may become even more entrenched when challenged. Coaches must generally be gentle in their approach to surfacing interference to learning and performance in an individual or team. Hints, suggestions, and indirect probing, though they may seem to take longer than a more direct approach, are usually more successful over the long run.
I learned a great deal about interference and how to help people work through it while coaching tennis and golf—two sports in which the obstacles to performance are difficult to disguise. And I have continued to find these sports excellent examples for exposing hidden obstacles to learning and performance. In addition, tennis and golf show the kinds of results that can occur when one succeeds in diminishing the impact of interference.
One of my favorite examples is what I call “the uh-oh experience.” A tennis ball is coming toward a player who thinks she has a weak backhand. As the ball approaches, she thinks.
“Here comes a probable mistake.” She tightens her muscles, steps back defensively as if to avoid the threat, then slashes jerkily at the ball. When this action results in either an error or an easy shot for the opponent, she confirms to herself, “I really do have a terrible backhand,” and unwittingly sets herself up for the same results on the next similar shot.
If a coach tried to correct each of the elements of the player’s stroke that were incorrect, it would take months of “learning.” However, if the coach worked at eliminating the player’s negative self-talk by focusing her attention instead on perceiving the details of the ball’s trajectory, most of the positive behavioral changes would take place without conscious effort. Working at changing a player’s perception instead of his or her behavior saves time and frustration for both student and coach.
Below is a partial list of obstacles to growing capability:
THE INNER GAME™
Every game is composed of two parts: an outer game and an inner game. The outer game is played in an external arena to overcome external obstacles in the way of reaching external goals; the inner game focuses on internal obstacles as well as internal goals. The Inner Game is an approach to learning and coaching that brings the relatively neglected skills from the inner game to bear on success in the outer game. Its principles and methods were first articulated in the best-selling sports book, The Inner Game of Tennis (Random House, 1974), and were expanded upon in Inner Tennis, Playing the Game (1976);Inner Skiing (1976); and The Inner Game of Golf (1979). The Inner Game of Work, based on my work with major corporations interested in more effective ways to grow the capabilities of their people, will be published by Random House in 1998.
- The assumption that “I already know.”Professionals often feel that they must present the appearance of already knowing everything and already being perfectly competent. This is an obstacle to learning that young children do not share.
- The assumption that learning means remediation. For many people, the suggestion that they should learn means there is something wrong with them or their level of performance.
- Fear of being judged. We learn this early, through teachers and parents who used judgment as a means to control behavior and effort.
- Doubt. The uncertainty we feel when we face the unknown is a prerequisite for learning. Young children are not embarrassed by not knowing something. However, as we age, we are taught to feel stupid or incompetent if we lack knowledge or experience or are unable to perform up to expectations. We are especially vulnerable to this feeling when faced with the challenge of unlearning something. The prospect of acknowledging that we might have invested time and effort in a perspective that is no longer valid can seem especially threatening.
- Trying too hard to learn and to appear learned. This phenomenon is a derivative of fear and doubt, and leads to constricted potential and mistakes. Our errors then confirm ours self-doubt and bring about the very outcome that we feared.
Revealing the barriers to learning and performance can be an important first step in maximizing an individual’s or a team’s potential. To find the greatest leverage for reducing obstacles to learning in the workplace, I believe we should start with our definition of work itself. The way we see “work” has an impact on how we perceive everything we do in the workplace.
What Is Work?
If you ask executives the meaning of the word work, they focus on work as doing something—as accomplishing a goal, such as providing a product or service. In other words, to many people, work means performance. But definitions that equate work with performance can be limiting, especially in the current business environment.
Are there other results of work? When I ask executives this question, they generally offer responses that refer to two other distinct aspects of work. One is the domain of experience: How you feel while working is also a result of work. While working, people feel satisfaction, meaning, accomplishment, and challenge, as well as frustration, stress, anxiety, and boredom. Everyone at work experiences feelings that range from misery to fulfillment.
A second set of answers fall into the category of learning: While working, you can grow, develop know-how and skills, and improve your ability to communicate, plan, and strategize. Like performance and experience, learning is a universal and fundamentally human result of work—people of all ages, cultures, and levels of expertise are either learning and growing or stagnating and “devolving” while working. Adults can learn while working, just as children learn naturally while playing.
The Work Triangle
How are these fundamental results of work—performance, experience, and learning—related? They are unquestionably interdependent. If individuals aren’t learning, their performance will decline over time; if their predominant experience of work is boredom or stress, both learning and performance will suffer. These three results can be represented in a mutually supportive “Work Triangle,” with performance at the apex, and experience and learning at the base angles (see “The Work Triangle” on p. 3).
When I ask a group of executives, “Which of the three work results gains the greatest support and encouragement in your work environment?” their response is overwhelmingly, “Performance.” I then place my marking pen at the center of the Work Triangle and slowly draw a line toward the performance apex. “How much more priority is performance given over learning and enjoyment?” I ask. As the pen reaches the top of the triangle, a voice usually says, “Stop there.” In response, the majority chants, “Keep going,” until the line has gone past the apex and is several inches outside the triangle. There is a general chuckle and a sense of a common understanding of corporate priorities.
In the competitive world of business, it is easy to see why performance may be given priority over learning and experience. But what are the consequences of pursuing performance at the expense of learning and experience? In any but the shortest timeframe, the consequences are dire: performance itself will fall. And what will be management’s typical response? More pressure on performance, resulting in even less time and fewer resources directed toward learning or quality of experience.
How does the emphasis on performance play out in practice? Take your average sales manager who meets weekly with his sales representatives. The conversation usually focuses on performance issues, such as, how many calls did you make? What were the results of those calls in terms of sales? What are your plans for next week?
But what if the manager were committed to his own learning, as well as to his team’s development? He might also ask: What did you find out from customers that you didn’t know before—about their resistances, their needs, their perception of our products, how we compare to our competitors? How are different customers responding to our latest promotion? Did you gain any insights into your own selling skills? What is the competition doing? What are you interested in finding out next week? Did you learn anything that might help others on the team?
Our definition of work should include the worker’s experience and learning, as well as his or her performance. The real value of this redefinition of work is that it includes me as an individual. I directly and immediately benefit from the learning and experience components of the Work Triangle. The “Experience” side of the triangle reminds me that I can’t afford to neglect personal fulfillment during my working hours in the hope of enjoying myself only during vacation time or on weekends. I can never replace the hours of my life I spend at work, so I need to make the most of them.
The “Learning” side of the triangle reminds me that my future work prospects depend on the growth in in my capabilities. Even if I’m fired from my present job, I take with me what I have learned, which I can leverage into productive and valued performance elsewhere. When my customers, managers, teammates, and the surrounding culture pressure me for performance results, the Work Triangle helps me remember that the person producing those results is important, too. I neglect my own learning and quality of experience at great peril to myself as well as to my future levels of performance.
The Tunnel Vision of Performance Momentum
The definition of work that focuses strictly on performance results at the expense of learning and experience produces a kind of tunnel vision that prevents workers from being fully aware and focused. I call this state of unconsciousness “performance momentum.” At its worst, performance momentum is a series of actions an individual performs without true consciousness of how they relate to his or her most important priorities. Some call this mode of operation “fire-fighting.” Examples include getting so caught up in a game of tennis that you forget it is a game, or engaging in conversations that undermine a relationship for the sake of merely winning an argument. In short, performance momentum means getting caught up in an action to the extent that you forget the purpose of the action.
I don’t know of a more fundamental problem facing workers today. When individuals are caught up in performance momentum, they tend to forget not only important performance goals, but also their fundamental purpose as human beings. For example, my need to finish an article by the requested deadline obscures the reasons I chose to write the article in the first place, and dampens the natural enjoyment of expressing my thoughts and convictions. The person caught up in performance momentum neglects learning, growth, and the inherent quality of the work experience.
THE WORK TRIANGLE
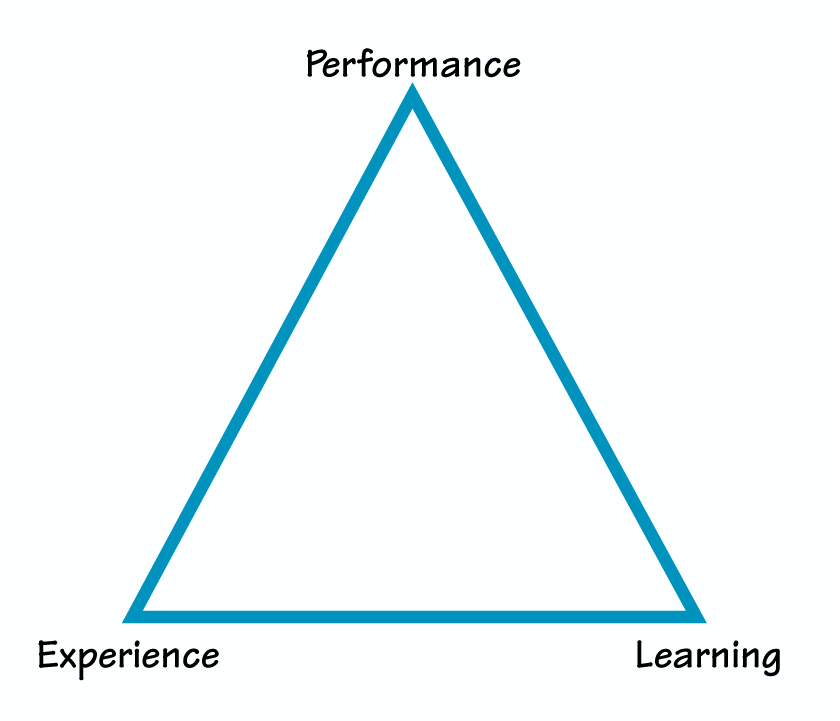
The fundamental results of work—performance, experience, and learning—are interdependent. If individuals aren’t learning, their performance will decline over time; if their predominant experience of work is boredom or stress, both learning and performance will suffer.
The tunnel vision that results from performance momentum is difficult to escape when individuals are working in a team that confirms and enforces the focus on performance. Any activity that is not seen as driving directly toward the goal is viewed as suspect. However, when a team or individual sacrifices the learning and experience sides of the Work Triangle to performance momentum, long-term performance suffers. More important, however, the individual suffers. And because the individual constitutes the building block of the team, the team suffers as well.
Balancing the Work Triangle
A simple method for assessing the balance among the three elements in the Work Triangle is to evaluate the way an individual or team articulates performance goals in comparison with learning and experience goals. It is revealing that many employees, when asked about learning or experience goals, are vague and express less conviction than when discussing performance goals. Setting clear learning goals is a good way to begin rebalancing the Work Triangle.
However, the distinction between learning and performance is often blurred. Even individuals who have worked on plans for the development of their competencies often fall into the trap of expressing their learning goals in terms of performance; for example, “I want to learn to focus more on the customer”; “I want to learn to reach higher sales quotas”; and“ I’m working on learning how to get a promotion. ”The general rule for distinguishing between learning and performance goals is that learning can be viewed as a change that takes place within an individual, while performance takes place on the outside. Learning is an increased capacity to perform; performance is the evidence that the capacity exists.
A good way to focus on learning goals is through the acronym QUEST.
Q—qualities or attributes you might want to develop in yourself or others
U—increased understanding of the components of any person, situation, or system
E—development of expertise, knowledge, or skills
S—capacity for strategic, or systemic, thinking
T—capacity to optimize what you do with time
Teams and individuals can use QUEST to help form goals regarding what capabilities they want to develop. To be most effective, these objectives should support immediate performance goals but at the same time apply to many future performance challenges.
Coaching: A Conversation That Promotes Learning
When executives list the qualities, skills, and expertise they want from employees, they often list intangible attributes, such as creativity, accountability, sense of humor, team player, problem solver, and so on. So, how can you get the qualities and capabilities you want from people? The first response to this question is usually, “We have to do a better job in hiring.” Clearly, it is important to hire capable people. But the real question is how to build the capabilities in the people you have hired, and how to keep those qualities from diminishing.
Unfortunately, the tools of managing performance are not particularly useful for promoting or developing important qualities and core skills. And it is difficult to imagine a course that teaches the rudiments of initiative or cooperation. So what is left? The word I use for the capacity to promote such desired attributes is coaching.
Coaching is a way of being, listening, asking, and speaking that draws out and augments characteristics and potential that are already present in a person. An effective coaching relationship creates a safe and challenging environment in which learning can take place. Coaches know that an oak tree already exists within an acorn. They have seen the one grow into the other, over time and under the right conditions, and are committed to providing those conditions to the best of their abilities. Successful coaches continually learn how best to “farm” the potential they are given to nurture.
A primary role of the coach is to stop performance momentum by calling a time out and providing questions or perspective that can encourage learning. Actual learning happens through experience—taking actions, observing the results, and modifying subsequent actions. To turn a work experience into a learning experience, a particular mindset must be established beforehand. Establishing this perspective can be done through something I call a “set-up conversation,” which an individual can conduct alone through self-talk or with a coach. The set-up conversation helps make the learner aware of the possibilities that the imminent work experience could yield. In conducting one of these conversations, the coach asks questions that aid in focusing the individual’s or team’s attention.
At the end of a work experience, the coach and individual can hold a “debrief conversation.” During this interchange, they might “mine” the gold of what was learned and refine questions to take into the next work experience. In this way, experience itself becomes the teacher. The coach’s role becomes helping the learner as valuable questions of the “teacher” and interpret the answers.
Coaching is very different from what we are generally taught as managers or teachers. We cannot teach work teams and individuals how to grow capabilities—in the sense of the transference of information in a class-room environment. Nor can we build capabilities through managerial techniques—for example, requiring certain abilities and rewarding employees when they display them or punishing them when they don’t. Neither can we measure learning, because we can’t directly observe it. In sum, it is the learner alone who controls the process and perceives its benefits. Managers don’t even need to reward employees for learning—if learning indeed takes place, it will lead to improved performance. And employers generally award bonuses, raises, and promotions based on an increase in a worker’s performance results.
Employees and managers cannot afford to wait for their corporate cultures to become learning cultures. Workers benefit from an expanded definition of work that includes learning and experience goals, and therefore must make the commitment to achieve those objectives. But companies also benefit from this new perspective on work. Wise are the corporate leaders who recognize that redefining work in this way is a difficult task, but that the company and its shareholders also gain advantages from a balanced Work Triangle. The best managers will provide what support and resources they can to the effort, and will make it their mission to shape their workplace into an optimal learning environment. The payoff will be improved business results and a corporate culture that attracts employees who equally value growth in capabilities.
Tim Gallwey is credited with founding the field of sports psychology. His four best-selling books on The Inner Game have deeply influenced the worlds of business and sports. For the last 15years, Tim has spent most of his time working with companies that want to find a better way to implement change. This article is based on a working progress called The Inner Game of Work, to be published in 1998 by Random House.
Editorial support for this article was provided by Janice Molloy.
