World events over the past several years have highlighted the need for new ways of exercising leadership. Such events include the ongoing crisis in the Catholic Church; ethical lapses in the business community; the war with Iraq and the continued violence in that country; and many others. In each of these settings, some of the responses by top leaders have appeared both arrogant and defensive, reactions that serve to exacerbate rather than resolve the situation. This stance — and the resulting cycle of betrayal, aggressive retaliation, counterattacks, and defensiveness prompted by fear and mistrust of the “other” is also one that many of us have encountered in our interactions with those in positions of authority in our work and community lives. But in an interdependent world in which dealing with “the other” is becoming increasingly inevitable, new approaches to leadership must evolve. Otherwise, we are bound to repeat the same patterns over and over again, with disastrous consequences.
In this changing world, it’s useful to think of leadership not as an immutable set of qualities but as an activity: the activity of engaging people to accomplish a common purpose. This process takes place within a particular social, political, economic, and technological environment — the features of which influence the effectiveness of certain styles and approaches to leadership. It is my contention that the environment has changed dramatically — in ways that I will describe more fully below — and that one of the new characteristics that leaders must adopt to be effective is that of vulnerability.
Vulnerability is not an attribute commonly associated with leadership. The word evokes images of weakness, fallibility, and defenselessness. Roget’s Interactive Thesaurus identifies nine synonyms for the word “vulnerability”: danger, dependence, exposure, infirmity, instability, jeopardy, liability, peril, and weakness. So why would anyone deliberately seek to be vulnerable? How can doing so possibly be necessary for leaders today? Isn’t living in the world dangerous and unstable enough without deliberately cultivating vulnerability? Before discussing these questions, let’s explore what I mean by “vulnerability” in the context of leadership.
The Discipline of Vulnerability
Pema Chödrön uses the metaphor of a room to describe how we often relate to the world. We create this room to suit us perfectly. It is the perfect temperature; the food is our favorite, as is the music. Only the people with whom we get along are allowed to enter this room. It is a wonderful environment, perfectly suited to us. But gradually the room turns into a prison as we become more and more afraid to venture out. The longer we stay in the room, the more threatening the outside So we take steps to for selves even more, padlocking the doors and shuttering the windows.
This is the position of too many leaders today. In a world full of perceived threats from all quarters, leaders tend to isolate themselves as they attempt to single-handedly eradicate all perils facing their organizations. In doing so, they cut themselves off from important sources of information and valuable relationships. In this new environment, the existing leadership paradigm — the “leader as hero” — serves as a prison.
As Chödrön says, “Staying in this room is not productive of being a whole, healthy, sane, well-adjusted person. . . . It’s not productive of awe, wonder, curiosity, or inquisitiveness. It’s not productive of tolerance, and it breeds bigotry and racial hatred.” And then she adds, “Our life’s work is to learn to open the door.” Learning to open the door — for individuals, organizations, and even nations — involves cultivating vulnerability.
In The Fifth Discipline, Peter Senge writes: “Each of the five learning disciplines can be thought of on three distinct levels:
- Practices, which are the things you do
- Principles, which are guiding ideas and insights
- Essences, which is the state of being of those with high levels of mastery in the discipline.”
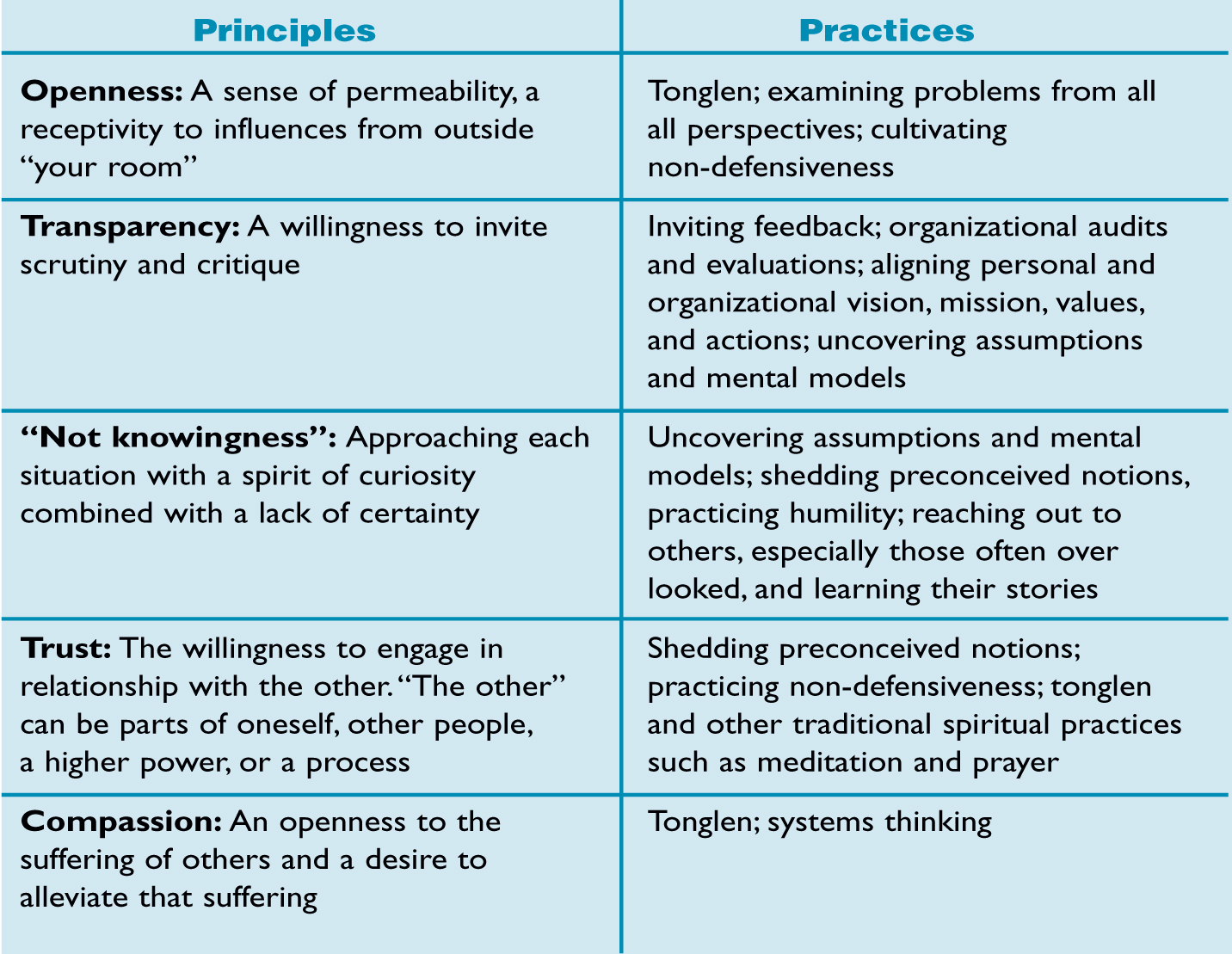
Using this framework, and thinking of vulnerability as a discipline, its essence is a sense of unguardedness and willingness to be changed. Principles or guiding ideas that support the discipline of vulnerability might include openness, transparency, “not knowingness,” trust, and compassion. Openness is a sense of permeability, a receptivity to influences from outside “your room.” Transparency is essentially a willingness to invite scrutiny and critique. “Not knowingness” is a bit harder to describe. The Zen Buddhist phrase “beginner’s mind” captures this principle well, in that it encourages us to approach each situation with a spirit of curiosity combined with a lack of certainty. “Not knowingness” is another form of openness — the openness to new ideas and ways of seeing the world. Trust involves yet another kind of openness — the willingness to engage in relationship with the other.
“The other” can be parts of oneself, other people, a higher power, or a process. Finally, compassion entails an openness to the suffering of others and the desire to alleviate that suffering. Embracing vulnerability through the application of these principles can be strengthened through a myriad of practices, some of which will be described later in this article.
The Call for Change
Why is vulnerability particularly relevant as a leadership discipline now? First, people around the globe are increasingly aware of the interconnectedness of all existence. Even in the most isolated settings, developments in communications technology have made it possible for people to quickly and easily learn about events occurring in other parts of the world. Such awareness then influences what they consider to be their sphere of concern. At the same moment, I can be troubled by the performance of my local school system, the bombing of the U. N. headquarters in Iraq, and the continuing heat wave in Europe. Knowing about these events inevitably expands my consciousness.
The globalization of the economy also compels individuals and organizations to operate as part of a larger whole. Even remote areas feel the economic impact of events occurring in other regions. For example, some months following the bombing of the World Trade Center, my husband and I were riding in a taxi on the Caribbean island of Saint Lucia. The driver started talking about September 11th and what a terrible thing it had been. As an American, I assumed that he was expressing his condolences for the loss of life in the U. S. As it turned out, his primary concern was the effect on his local economy of the drop in air travel following the attacks. This incident is but a small example of the powerful web of economic interconnectedness that characterizes our time.
Additionally, we have become increasingly consciousness of the interconnectedness of systems that were once perceived and treated as substantially separate. For example, there is more and more evidence that the phenomenon of “urban sprawl” contributes to a diminished sense of community and environmental degradation. When people must get in their cars and drive in order to carry out their daily activities, they no longer
Although the “leader as hero” may never be completely replaced, we now have other models to guide our behavior.
casually encounter fellow community members and they contribute to environmental pollution. Other examples abound. It is too early to know whether our rising awareness in this area will lead to changes in practices, but further progress will certainly be aided by a stance of vulnerability.
A second condition that calls for leaders to adopt a stance of vulnerability is the tarnished credibility of many major institutions, including the media, the church, and the marketplace. This may be a “good news, bad news” occurrence, setting the stage for citizens to require their leaders to act with humility, transparency, and trustworthiness. At this writing, it is hard to know what direction society will take: a flurry of laws, litigation, reorganization, and regulations intended to prevent such violations from recurring, or a more fundamental revisiting of our basic expectations about social institutions and their leaders.
A third condition, which is a potentially positive development, is an emerging civic re-engagement movement that seems to be gaining momentum. One example is the powerful Internet-based citizen participation vehicle “Move On,” which aims to “bring ordinary people back into politics.” It currently has an international network of more than two million online activists, which has taken action on a variety of political and social issues since 1998. In addition, more and more opportunities exist for large numbers of citizens to engage in dialogue and offer their views on important public developments. One such example was the historic “Listening to the City” event held in July 2002, in which 5,000 New Yorkers offered comments on plans to redesign lower Manhattan, rebuild the World Trade Center, and create a memorial for the victims of the September 11th attacks.
As a facilitator of this session, I was profoundly impressed by both the skillfulness of the process and the quality of the results. This event required a stance of vulnerability from everyone involved. Those who commissioned the process remained open to being influenced and were willing to modify the outcome to reflect the needs expressed by participants during the day-long event. Those who attended the gathering demonstrated trust that their input would be taken seriously, even as they entered into the dialogue with self-described “New York cynicism.” Those who organized the process were flexible and willing to make changes in real time, for instance, when the majority of participants balked at taking part in one planned exercise. The gathering truly demonstrated the qualities of vulnerability described in this article and, indeed, had an impact on the course of the rebuilding process.
A final condition brings us back to the point made earlier: that desirable leadership attributes will be influenced by the environmental context. In order to help leaders to operate effectively in this complex, interdependent, and heterogeneous environment, scholars are articulating a new image of leadership. Recent books such as The Spirit of Leadership by Harrison Owen (Berrett Koehler, 1999), Leading Without Power by Max De Pree (Jossey-Bass, 1997), and Leading Quietly by Joseph Badaracco, Jr. (Harvard Business School Publishing, 2002) emphasize the relational, subtle, and even spiritual elements of modern leadership. Increasingly, the inner work of leadership is being linked to outer actions. Although the “leader as hero” may never be completely replaced, we now have other models to guide our behavior.
Taking Off the Armor
“You become what you practice most.” — Unknown
It is difficult to expect leaders who have not embraced the discipline of vulnerability throughout their careers to do so when the stakes are high. Instead, leaders must consistently cultivate this approach over the long term. Pema Chödrön writes, “When I was about 12, I read a Life magazine series, ‘Religions of the World.’ The article on Confucius said something like: ‘By the time you’re 50, if you’ve spent your life up until then taking the armor off . . . then you’ve established a pattern of mind that for the rest of your life, you won’t be able to stop. You’ll just keep taking the armor off. But if by the time you’re 50 you’ve become really good at keeping
THE PRINCIPLES OF VULNERABILITY
that armor on . . . it’s going to be very hard to change.”
Regardless of our age or position in our organization, how might we start to “take off the armor”? We can begin with the principles of vulnerability outlined above: openness, transparency, “not knowingness,” trust, and compassion. For each of these guiding ideas there are numerous practices that run the gamut from audits to Zen. Below are examples of some that might support each of the principles (also see “The Principles of Vulnerability”).
Openness. A number of years ago, I attended a barbecue hosted by a local police officer, along with mutual friends. This was the first time we had met most of the people at this party. Early in the evening, our host began railing against the Puerto Ricans who had moved into his community in recent years. He described them as having caused an increase in crime, poverty, and teen pregnancy in the town. My first instinct was to react to aggressively defend the people he was maligning — but we were his guests and it did not seem appropriate. I was greatly conflicted: I felt as though his beliefs, his perspective, would seep into me and become a part of my identity if I didn’t mount a defense. But as a guest and a stranger, I did not feel it was polite to argue with him.
Instead, I tried to be open to his perspective. When I actually allowed myself to take in his point of view, I realized that police officers regularly encounter people at their worst. Given that, why would he have a different perspective about Puerto Ricans? Once I became vulnerable and considered his perspective, it changed me.
At that point, I began to pay attention to the ways in which my fear of being “colonized” by “the other” was causing me to become rigidly defensive of my own views. I started exploring various practices that enhance individual and collective openness. The Buddhist practice of tonglen, which means “exchanging oneself for the other,” is a powerful personal discipline for cultivating compassion and a sense of connection with others. Tonglen entails the deliberate “breathing in” of someone’s pain, anger, sadness, and negative energy and “breathing out” light, warmth, and positive energy directed toward that individual. I have found it to be especially helpful in countering the tendency to defend my own beliefs and reject those of other people.
There are also numerous exercises that encourage taking different perspectives, including the exercise called “Multiple Perspectives” described in The Fifth Discipline Fieldbook. The exercise, which is useful for teams working on a real problem, involves identifying each of the stakeholders and rotating among roles in order to see the issue from as many vantage points as possible. This exercise can benefit individual participants as well the team as a whole.
The June 2003 issue of Fast Company magazine features an organizational example of the power of taking multiple perspectives. The Dofasco Steel Company of Hamilton, Ontario, has distinguished itself because of its emphasis on the “triple bottom line” (society, the economy, and the environment) as well as its consistent profitability, in an industry where neither are typical. Former CEO John May berry says, “These things all bleed into each other. How do you get happy shareholders? Start with satisfied customers. How do you get satisfied customers? Start with happy employees. How do you please employees? Try not to wreck the community they live in.” When faced with seemingly incompatible goals, such as reducing energy consumption while still producing high-quality steel, the company creates innovative solutions by “constantly examining problems from all perspectives as we try to solve them. And often, an improvement in one area that might initially look bad for another stakeholder actually pushes you to come up with solutions that are better all around.”
Transparency.
Individuals and groups alike can practice transparency, the openness to scrutiny or critique. On an individual level, we can invite friends, family members, and colleagues to offer feedback about our behavior and its impact on them. We can also make ongoing efforts to align our purpose, values, and goals to result in more consistent actions. If others know what our values are and can observe a pattern of behavior consistent with those values, then the reasons for our actions are clearer than they might have been if we behaved in inconsistent and unaccountable ways. Any effort to bring to consciousness our own mental models and assumptions, along with the willingness to make those public, is practicing transparency.
For organizations, one powerful way of practicing transparency is by inviting scrutiny — feedback — from outside parties through external evaluations and audits. Recently, the food industry, spearheaded by the Food Marketing Institute and the National Council of Chain Restaurants, implemented an animal welfare initiative that is producing audits of eggs, milk, chicken, and pork producers and will eventually result in inspection of cattle and feed lots. In 1997, McDonald’s restaurant began a process that eventually required all of its meat producers to undergo animal welfare audits: In 2002, it conducted 50 such audits worldwide.
Other ways in which organizations can practice transparency include aligning vision, mission, values, goals, and practices and collectively uncovering assumptions and mental models. The Fifth Discipline Fieldbook and other resources describe a number of techniques for creating a shared vision and uncovering mental models. Although the techniques are well proven, they are most successful in environments in which there is already a fair amount of openness and trust.
For a variety of reasons, having the answers can be the most unhelpful thing a leader can do.
“Not Knowingness.” People in leadership roles are often expected to have all the answers. In fact, for a variety of reasons, having the answers can be the most unhelpful thing a leader can do: It allows others to avoid taking responsibility; it perpetuates the “leader-as-hero” myth; it suppresses creative thinking that can come from those on the margins; and it keeps others at a distance. “Not knowingness” requires especially rigorous practice because the pressure that leaders experience “to know” comes both from within and without.
Leaders who want to adopt this principle might find inspiration in the experiences of former Hewlett-Packard executive Greg Merton. In his article, “Leadership is Sourced by a Commitment to Personal Development” (Reflections, Fall 2002), he writes, “I am learning that a willingness to be vulnerable arises out of strength, not weakness. We protect ourselves out of fear, not confidence. And if we want those around us to learn, then we must be learning as well.”
The creation of the Grameen Bank in Bangladesh is an excellent example of “not knowingness.” Since the early 1980s, this bank has made a success of doing something no other bank has done: lending to the poor. In Reflections (Spring 2002), the leader of the bank, Muhammad Yunus, described its origins. Conditions in Bangladesh in the mid-1970s were horrific. As Yunus walked from his beautiful bungalow to the university where he was teaching economics, he would pass by people dying in the street. He realized that his economic theories were useless in the face of those conditions. He said, “I felt completely empty. . . . I realized I could help people as a human being, not an economist. So I decided to become a basic human being. I no longer carried any preconceived notions.”
Stimulated by this realization, he traveled into local villages to learn about poverty by listening to poor people themselves. He discovered that many of them earned a meager income by making things to sell but, in order to buy the raw materials, they had to borrow cash from a moneylender at high interest rates. Making these payments left them without enough money to live on. The people Yunus met were not victims or malingerers; they were motivated entrepreneurs who lacked resources. This learning became the foundation of the creation of Grameen Bank, which has grown to be an international model for microcredit banks, lending money to people with no collateral.
Trust. “Not knowingness” also involves a willingness to trust an unfolding process and to have a kind of faith, whether it is faith in other people, in oneself, in a deity, or merely in the integrity of the outcome. In A Path with Heart (Bantam Books, 1993), Jack Kornfield includes a wonderful story about Vinoba Bhave, who was Gandhi’s closest disciple and heir apparent. After Gandhi’s death, his followers tried to convince Vinoba to lead a nationwide convention to decide how to continue Gandhi’s work. With serious reservations, Vinoba agreed, but only on the condition that the conference be postponed for six months so he could walk there on foot, halfway across India.
In his travels, Vinoba discovered the same scenario in village after village: The people were poor and were unable to grow their own food because they owned no land. At first, he promised to talk to Prime Minister Nehru about passing a law to give land to the poor villagers. Upon reflection, he realized that such a law would be ineffective in addressing the problem because it would take years to pass and when it was finally put into place, corrupt governmental officials would siphon the land grants away before they ever reached the people. Sadly, he gathered a group of villagers together and told them his conclusion.
In response, one rich villager pledged to give some of his land to 16 families, each of whom needed five acres. This generous offer prompted others to follow suit in village after village as Vinoba traveled to the conference. During his journey, he stimulated the transfer of more than 2,200 acres of land to poor families. As a result, others joined the effort, which became known as the great Indian Land Reform Movement.
Kornfield writes, “All of this began from a spirit of listening, a caring for truth, and a compassionate beginner’s mind brought to an old and difficult situation.” I would add that it also came from a trust in an unfolding process. If Vinoba had proceeded with an agenda, clear goals, and a decisive vision of the future of the Gandhian movement, would the Indian Land Reform Movement ever have happened?
Compassion. Compassion is defined as “deep feeling for or understanding of misery and suffering and a desire to promote its alleviation.” It results from the act of “opening the door” discussed earlier in this article. The spiritual practice of tonglen is deliberately aimed at cultivating compassion.
Whether we use a spiritual or cognitive route to expand our perception of the interconnectedness of elements within systems, we cannot fail to experience a strengthened relationship with the other parts of that system: individuals, work groups, organizations, cultures, nature, and so on. Awareness of this relationship creates the groundwork for a compassionate response to the other. Peter Senge quotes Einstein on this topic:
“[The human being] experiences himself, his thoughts and feelings as something separated from the rest — a kind of optical delusion of our consciousness. This delusion is a kind of prison for us, restricting us to our personal desires and to affection for a few persons nearest to us. Our task must be to free ourselves from this prison by widening our circle of compassion to embrace all living creatures and the whole of nature in its beauty.”
The practice of systems thinking can enable us to see the interconnection between elements that had previously been perceived as separate. Systems diagrams can be a useful tool for cultivating this type of thinking. In a leadership course I was teaching for people with mental retardation and their workers, we used a rudimentary systems diagram to describe the relationship between the behavior of staff and clients in a group home. One of the residents understood the connection immediately: “So when staff yell at me, then I feel ashamed and that makes me mad and I yell back. The staff think I’m acting out and then they restrain me.” Through the practice of systems thinking, this participant, who had previously viewed interactions entirely from her own perspective, was able to take the perspective of others. This stimulated a thoughtful discussion about the ways in which the behavior of the staff and residents influenced each other, which helped to break down barriers between people in those two roles.
Perhaps a case study will be useful at this point. What follows is a real situation.
In the mid-1990s, a small town in a rural state experienced a series of violent events that challenged the community’s capacity to act compassionately toward individuals with mental illness. The incidents also challenged the state mental health department to operate with a stance of vulnerability rather than the usual defensive posture that is so prevalent in response to scandal. First, a man with a history of mental illness attacked members of a local religious order; two of these women subsequently died. The man knew these individuals and had grown up in the community. Several months later, another murder took place in the town; the alleged perpetrator was on a waiting list for mental health services. During the same year, in a nearby town, a resident of one of the state-run psychiatric facilities was murdered by her boyfriend.
Any one of these tragic events might have provoked a serious backlash against the mental health department and the people it served. The coincidence of three violent crimes happening within a short timeframe was a recipe for disaster. It would not have been surprising to find the system’s leaders engaging in defensive practices such as scapegoating, retreating, and retaliating. Instead, leaders within the system chose to stay focused on the circumstances of the people they served and the well-being of the community at large, a focus that necessitated a different set of responses than the conventional ones.
What did the department actually do? In the instance of the nuns’ murder, the department reached out to those people who had a stake in the unfolding events. First, officials asked themselves, “Who is going to be most affected by this horrible incident and its potential implications?” They contacted the head of the local chapter of AMI, a national education and advocacy group for people with psychiatric disabilities and their families. They also got in touch with the leader of the local mental patients’ advocacy movement, the mayor of the community, the head of the agency that served the perpetrator, and the Catholic diocese. This group of people from the community got together and said, “Our community has a reputation as a caring community, and we need to let people know we are not going to scapegoat people with mental illness or let this become a witch hunt. That’s not what this community is all about.”
Although the event and its aftermath were tragic and painful, the behavior of this community group, supported by leaders within the mental health department, prevented worse consequences. In fact, a reporter who had grown up in the community returned to his hometown shortly after the attack to see what the effects had been. Fully expecting a severe backlash against people with mental illness, what he found was very different. Four days after the incident, 1,000 citizens crowded into a church just down the street from the convent for a public prayer service. The town’s mayor urged them to pray for the family of the perpetrator. The state legislature later called for improved treatment of mental patients living in local communities. The nuns continued to pray for the man who had killed two of their own.
How does this example illustrate the discipline of vulnerability? Instead of padlocking the door, turning off the phones, and hunkering down in their “room,” the department heads acknowledged that they needed to work with other key stakeholders. They recognized that they were but one element of a larger system, and possibly not even the central or most relevant one. Instead of protecting and defending itself, the department reached out to others. Its message was, “We need you; we can’t do this alone.” Given that department leaders were besieged by lawsuits and attacks in the newspaper, actions that often lead people to feel defensive, it is all the more remarkable that they chose to respond in this way.
Further, the department proceeded with a sense of not knowing, a courageous stance for an institution expected to wield power, expertise, and accountability. Leaders focused on creating an expansive, long-term agenda, rather than on merely reacting to the crisis. This approach enabled the broader group of stakeholders to establish common ground. It would have been impossible for them to do so if the emphasis had been on defending the stakeholders’ individual actions regarding the specific incident. Instead of fortifying their “room,” these courageous folks opened the door and went out into the world, vulnerable and open to influence. This is a clear example of the discipline of vulnerability at work.
A Fresh Approach
I have attempted to describe some current conditions that call for a stance of vulnerability and to describe why vulnerability is a core leadership discipline for these times. Although it may not be the most accurate term for what I have tried to describe, it does have the advantage of freshness. Using “vulnerability” as a positive term, a condition to which leaders might aspire rather than eschew, invites reflection upon our existing assumptions about leadership. Because I also wanted to include some practical elements, I have attempted to touch on some of the ways in which an individual or collective might cultivate vulnerability. Anyone interested in further pursuing these practices will find ample information else-where. My main hope in writing this article is that it might contribute to our individual and collective capacity to “open the door” and venture out into the world.
NEXT STEPS
- Explore your existing myths and assumptions about leadership. What is your current “job description” for a leader? In what contexts is it most effective? Where are its limitations most striking? Assess current events in terms of the skillfulness of the leadership being exercised.
- Become increasingly mindful of the tendency to retreat into “your room” through defensive actions. What circumstances prompt such a response? Practice staying open: What happens?
- Identify one area that you believe would enhance your organization’s practice of vulnerability. Find two co-workers who would be receptive and develop a strategy to make progress in this arena.
