Consider all the learning that occurs as people move from place to place inside and outside an organization, carrying insights and ideas from one conversation to another. The invisible connections among these conversations and the actions that emerge from them help to build the organization’s collective
CONVERSATION AS A PATH TO LARGE-SCALE CHANGE
knowledge and shape its future. But the process of co-creating the future through conversation is so natural we usually overlook it.
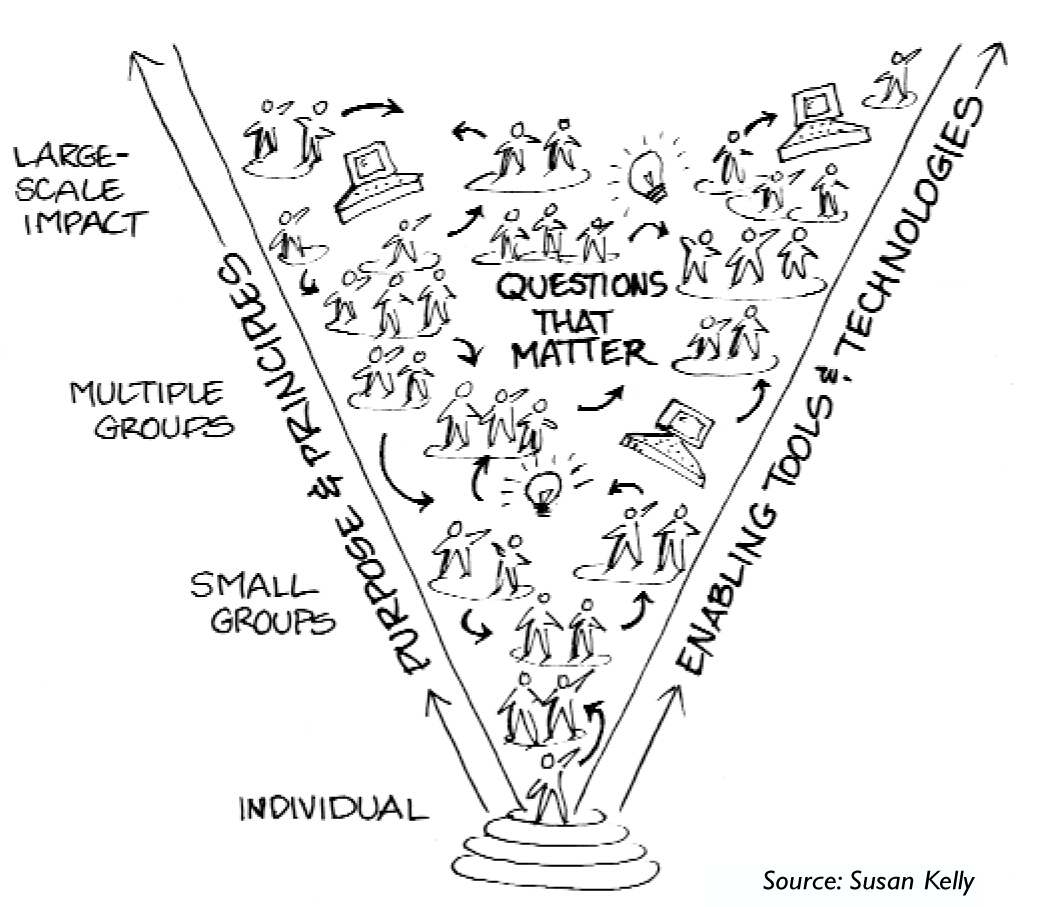
Since our early ancestors gathered in circles around the warmth of a fire, conversation has been a primary process for making sense of our world, discovering what we value, sharing knowledge, and imagining our future. Small groups exploring important questions — and connecting with other groups that are doing the same — have always played a major role in social and institutional renewal. Consider the sewing circles and “committees of correspondence” that helped birth the American Republic; the conversations in cafés and salons that spawned the French Revolution; and the Scandinavian “study circles” that stimulated an economic and social renaissance in Northern Europe. Reaching out in ever-widening circles, members of small groups spread their insights to larger constituencies, carrying the seed ideas for new conversations, creative possibilities, and collective action (see “Conversation as a Path to Large-Scale Change”).
Today, especially with the advent of the Internet, we are becoming increasingly aware of the power and potential of these dynamic networks of conversation and their systemic importance for large-scale collaboration, learning, and change. The crosspollination of ideas from group to group can lead to the emergence of surprising creativity and focus as we discover innovative ways to support a “system thinking together.”
What if we could create an intentional, simple, and effective approach for fostering greater collaborative learning and coherent thought than is often available in large group settings? Our research reveals that what we have come to call “The World Café” has a unique contribution to make when the goal is the focused use of dialogic inquiry to foster collective insight around real-life challenges and key strategic questions at increasing levels of scale.
What is The World Café? It is an innovative methodology that enhances the capacity for collaborative thinking about critical issues by linking small group and large-group conversations. In the process, knowledge grows, a sense of the whole becomes real, and new possibilities become visible. The World Café utilizes the principles of dynamic networks and living systems to access a source of deeper creativity and shared knowledge that might not be available through more traditional approaches to collaborative work.
The World Café is also an evocative metaphor that enables us to pay attention to aspects of organizational life that are often invisible, hidden by formal structures and policies. It highlights the naturally occurring networks of conversation and social learning through which we access collective intelligence, create new knowledge, and bring forth desired futures. Using The World Café as an organizing image allows leaders to intentionally design processes that take advantage of the natural dynamics that are already at play in order to create sustainable business and social value.
How The World Café Was Born
Several years ago, we serendipitously discovered the unique power of Café style conversations. One rainy morning, we wanted to provide a comfortable setting for participants in a global dialogue on intellectual capital to enjoy their coffee while waiting for the session to begin. We set up small tables in our living room and covered them with paper tablecloths. We added flowers and set out colored crayons, like in many neighborhood cafés.
People were delighted and amused. They got their coffee and gathered in small, informal groups around the tables. Soon, everyone was deeply engaged in conversation. As they talked, people scribbled ideas on the tablecloths. After a while, someone expressed curiosity about what was happening in other conversations. One person agreed to stay at each table as a host while others traveled to other tables to discover what interesting ideas were pollinating there.
People buzzed with excitement. At a certain point, they decided to leave a new host at each table. The other members traveled to new tables, connecting ideas, testing assumptions, and adding to each other’s diagrams and pictures on the tablecloths.
As lunchtime drew near, we took a “tour” of all the tablecloths, seeing what new connections and questions had emerged. Our interactive graphics specialist captured collective insights from the morning on a large piece of newsprint in the middle of the room. We suddenly realized that we had tapped into something very simple but potentially very powerful. Through the Café conversations, a shared knowledge base, larger than any individual or group in the room, had become accessible to us. Our unique contributions had combined and recombined into rich new patterns of living knowledge and innovative thought that had not been visible when we started.
CAFÉ HOSTING TIPS
- Set up Café-style tables or another relaxed setting.
- Provide food, beverages, music, art, natural light, and greenery.
- Encourage informal conversation focused on key questions.
- Allow time for silence and reflection.
- Encourage members to “cross-pollinate” ideas and insights across groups.
- Have materials available for visually representing key ideas — markers and paper.
- Weave and connect emerging themes and insights.
- Honor the social nature of learning and community building.
- Help members notice that individual conversations are part of and contribute to a larger field of collective knowledge and wisdom.
The World Café As Methodology
What makes such a seemingly simple practice — that of talking together about things we care about and intentionally linking the essence of our conversations with others in ever widening circles — so useful? We think it’s because Café conversations offer us the opportunity to notice the possibilities for mutual insight, innovation, and action that are already present in any group, if we only knew how to access them. We are discovering that this process offers a unique mixture of freedom and focus, of coherence without control. Depending on an organization’s needs, Café events can be designed around particular themes or topics. The Café format is flexible and adapts to different circumstances, based on a few simple practices and principles (see “Café Hosting Tips”).
Groups as small as 12 and as large as 1,200 from around the world have engaged in Café learning conversations in a wide range of settings. In a global consumer products company, executives from over 30 nations used Café principles to integrate a new worldwide marketing strategy. In New Zealand, Maori leaders combined The World Café with indigenous meeting formats during regional treaty negotiations. Mexican government and corporate leaders applied The World Café to scenario planning. A Fortune 100 company is using “Creative Cafés” to explore corporate responsibility with stakeholders. And faculty members in the U. S. and Europe are creating virtual online “Knowledge Cafés” to conduct distance-learning programs.
After participating in Café conversations, members share comments such as, “I developed productive relationships and learned more from others than I ever expected. You can actually see the knowledge growing.” Participants often develop an increased sense of responsibility for making use of the practical insights they gain and for staying connected as they expand the conversation to larger constituencies.
The practice of The World Café is based on a set of working assumptions that we continue to explore:
- The future is born in webs of human conversation.
- Compelling questions encourage collective learning.
- Networks are the underlying pattern of living systems.
- Human systems — organizations, families, communities — are living systems.
- Intelligence emerges as the system connects to itself in diverse and creative ways.
- We collectively have all the wisdom and resources we need.
Five Key Operating Principles
We are discovering that the unique contribution of Café learning seems to come from translating these working assumptions into the following five operating principles that, when used in combination, increase the likelihood of generating breakthrough thinking.
Create Hospitable Space. Café hosts around the world emphasize the power and importance of creating a welcoming environment to enliven collaborative conversation. We thrive and are better able to confront difficult questions, explore underlying assumptions, and create what we care about in surroundings that evoke warmth, friendliness, and authenticity than in those that are less hospitable to the human spirit. Most meeting places are sterile, cold, and impersonal. Consider choosing environments with natural light. Create comfortable seating. Honor our traditions of human hospitality by offering refreshments. Play soft music as people enter. Decorate the walls with art. Hospitable space means “safe” space — where everyone feels free to offer their best thinking.
Hosts can create hospitable space even in large, impersonal venues. For instance, at a conference for 1,000 people, we asked the hotel staff to set up small, round cocktail tables instead of rows of chairs in the cavernous ballroom. We then decked out each table with a red-checked tablecloth and a vase of red and white carnations. Volunteers placed sheets of white paper over the tablecloths and left small containers of colored markers for doodling. We also brought in palm trees and other greenery. When people entered the room, they were greeted by soft jazz music. The buzz of conversation almost instantly filled the space.
Knowledge emerges in response to compelling questions that “travel well” as they attract collective engagement and exploration throughout a system.
Explore Questions That Matter. One of our most important learnings in working with The World Café is that discovering and exploring “questions that matter” opens the door to catalytic conversation, insight, and innovation. Knowledge emerges in response to compelling questions that “travel well” as they attract collective engagement and exploration throughout a system. Powerful questions provide focus and coherence to networks of conversation that might otherwise spin off in random directions. Well-crafted strategic questions define intention, focus energy, and direct attention toward what really counts.
Hone the skill of shaping open-ended questions that are relevant to the group’s real-life concerns. These questions need not imply immediate action steps or problem solving. Allow the questions to invite inquiry and exploration. At one Café in Denmark focused on improving a school system, the hosts framed the central question as “What could a good school also be?” rather than as “How can we fix the problems in this school?” In doing so, they opened up the conversation to appreciating what might be possible in the future, rather than limiting the focus to what is wrong in the present.
Connect Diverse People and Perspectives. “Intelligence emerges as the system connects to itself in diverse and creative ways,” according to Margaret Wheatley, author of Leadership and the New Science (Berrett-Koehler, 1992). By cross-pollinating ideas among tables in several rounds of conversation, we intentionally invite a more accelerated and richer network of dialogic interactions on a larger scale than is common in most dialogue circles.
One technique for enriching the ways in which the system connects to itself is to vary the different rounds of conversation. Hosts stay at each table to welcome guests while the other members travel to new tables to share as well as gather insights. Travelers might then return to their home Cafés or continue to move from table to table for several iterations. Sometimes the hosts change, with the first host becoming a traveler during the second cycle. Or several members might stay at the table while the others go out for brief visits as “ambassadors” to other tables, collecting new seed ideas that bring diverse perspectives to the home table.
Additionally, all living systems — including human systems — benefit from diversity. In her book The Quantum Society: Human Nature and Consciousness Defined by the New Physics (William Morrow and Company, 1994), Danah Zohar states: “Social evolution requires that different points of view, different ideas, different ways of life, and different traditions recombine into larger, more complex emergent wholes.” Breakthrough thinking is more likely to emerge when diverse viewpoints and perspectives contribute to the exploration. For example, “Strategy Cafés” that engage multiple stakeholders, including employees from all levels as well as customers and suppliers, can offer richer opportunities for innovation than traditional strategic planning activities among senior executives alone.
Listen Together for Patterns, Insights, and Deeper Questions.
Through Café conversations, participants often discover coherent patterns of meaning in what may appear, at first glance, to be a chaotic and messy self-organizing exchange of ideas and perspectives. The emphasis is on shared listening — listening for the wisdom or insight that no individual member of the group might have access to by themselves. To that end, invite members to offer their unique perspectives and listen for new connections in the “space in-between.” Allow for silence and reflection. Ask members to notice what’s evolving in the middle of the table. By focusing on these special qualities of collective attention, we have a greater opportunity to experience what our Danish colleague Finn Voldtofte calls “the magic in the middle.”
For example, in Sweden, hosts of a multi-stakeholder forum used Café conversations to clarify areas of inquiry that could influence the future of both the information/communications industry and the environment. They began the first round of conversation by giving each table of participants a “talking stone.” Each member took the talking stone in turn and presented his or her key insights, thoughts, or deeper questions about the query “How can information technology contribute to a sustainable future?”
The three other participants at each table were to listen carefully and draw any connections they noticed between ideas in the middle of the tablecloth. In the second and third rounds, the Café hosts asked everyone to begin listening as a group for the deeper assumptions underlying their perspectives and to write them on the tablecloth as well. When the final round was over, the group pooled the collective insights and “ahas” that had emerged from linking the small-group dialogues from Café tables and creating a “conversation of the whole.” Through this intentional process of discovering and connecting underlying assumptions and insights, participants who might have opposed each other in a different setting came to a mutual appreciation of the deeper questions they faced together in contributing to a sustainable future.

Make Collective Knowledge Visible to the Group. We’ve come to realize that the simple act of scribbling ideas and pictures on a paper napkin or tablecloth so that the others at the Café table can literally “see what you mean” is integral to knowledge creation and innovation. As Michael Schrage says in Shared Minds: The New Technologies of Collaboration (Random House, 1990), “The images, maps, and perceptions bouncing around in people’s brains must be given a form that other people’s images, maps, or perceptions can shape, alter, or otherwise add value to. . . . It takes shared space to create shared understanding.” By providing paper and markers, we encourage the use of “shared space” where people can build on each other’s ideas, weave together their thoughts, and engage in deeper collective listening.
Many Café events include an interactive graphics specialist, who creates large visual maps that synthesize key insights and ideas. Commented Nancy Margulies, who has hosted many Cafés, “It’s like having a big ‘tablecloth’ in the middle of the whole group. Participants can quite literally see that they are creating something new together.” Other possibilities for making collective knowledge visible include having a “gallery walk,” with participants taking a tour of the tablecloths created by the different groups; publishing a Café newspaper on the spot; and creating theater presentations that reflect group discoveries. Each of these techniques allows participants to capture and build on the momentum and ideas that emerge. In addition, creating “storybooks” from the session allows participants to take the results of their work to larger audiences after the event.
The five operating principles seem quite simple, but embodying them as an integrated practice demands creativity, thoughtfulness, artistry, and care. The creativity of the host can make the difference between an interesting conversation and the magic of experiencing what our colleague Tom Atlee calls co-intelligence in action.
Conversation As Action
But is all of this talk just that, talk? What about the urgent need for action in our organizations today? We have found that, by its nature, The World Café challenges the ways most of us think about creating desired results in organizational and community life. Many leaders still preach that we should “stop talking and get to work” — as if talk and work were two separate things. Humberto Maturana, a pioneering evolutionary biologist, has helped us see that human beings think together and coordinate action in and through language. Conversation is “real work.” Through conversation people discover who cares about what and who will be accountable for next steps. We are finding that when people come to a new level of shared understanding around real-life issues, they want to make a difference. When participants return from Café conversations, they often see additional action choices that they didn’t know existed before.
Café As Metaphor
As reported by members of Café events, The World Café is a powerful methodology for collaborative learning and knowledge evolution. We are also finding that it is a provocative metaphor that can help us see organizational and societal change in a new light. How might the metaphor of “The World as Café” invite us to think differently about ways to catalyze system-wide innovation and action?
We are learning that Café conversations are based on a larger natural process of mutual inquiry and discovery that does not depend on small, round tables and red-checked tablecloths. By experiencing the power of focused networks of conversation on a small scale, members see how they might utilize this strategic insight in the larger systems they are part of. What if conversation were as much a core business process as marketing, distribution, or product development? What if it were already the core process — the source of organizational intelligence that allows all of the others to generate positive results?
For example, imagine your organization as a series of Café tables, with employees moving between functions inside the organization as well as connecting with multiple “tables” of customers, suppliers, distributors, and other conversation partners. What difference would it make to your own action choices if you viewed your workplace as a dynamic, living network of conversations and knowledge creation rather than as a traditional hierarchy (see “What We View Determines What We Do”)?
Based on an understanding of The World Café, leaders can take greater responsibility for designing infrastructures that bring coherence and focus to organizational conversations. For example, they come to recognize the key role they play in discovering “the big questions” and hosting strategic conversations with multiple stakeholders. This shift of lens also has practical implications for how leaders work with strategy formation, organizational learning, information technology, the design of physical space, and leadership development.
In one Café session, senior leaders from major corporations were mapping the implications of taking this view. The director of global operations for a company with more than 50,000 employees suddenly jumped up from his seat and exclaimed, “Do you know what I’ve gone and done? I’ve just reorganized my entire global operation. I’ve broken up the informal knowledge networks and relationships that have developed over the years. If I had looked at my reorganization through these glasses, I would have done it a lot differently. It’s going to take us a long
WHAT WE VIEW DETERMINES WHAT WE DO
-
- What is the unique contribution of leadership?
- What learning tools/methods/approaches have the most leverage?
- What are the implications for strategy evolution?
- How might you design physical space differently to support knowledge sharing?
- How would you approach the process of organizational change and renewal?
- What is the most strategic use of information technology?
- What are the indicators of success?
time to recover!” His heartfelt comments stimulated a lively conversation about the role of leaders in developing organizational strategies that honor these less visible but critical conversational and learning processes.
We’re seeing many practical examples of how people are intentionally using the metaphor of The World Café to guide strategic work in larger systems. Executives in a high-tech corporation helped to decrease the injury rate dramatically by using Café principles to engage existing networks of conversation and introduce questions about safety risks. The World Café has led intellectual capital expert Leif Edvinsson of Sweden to observe that the office design of the past is inadequate to support effective knowledge work. In response, he has engaged leading-edge architects in alternative space design.
World Café principles are also being used to redesign a Museum of Science and Industry in Florida to highlight not only formal exhibits but also learning conversations as doorways to discovery. And the initiative From the Four Directions: People Everywhere Leading the Way is intentionally weaving a global network of conversations among leaders of all ages on several continents. Using the Internet and other information technologies, local conversation circles feed insights back into the network, catalyzing these worldwide leadership dialogues into a growing force for societal innovation.
Creating Sustainable Value
The World Café is one path for stimulating courageous conversation about questions that matter to our lives and work—especially in large group settings. We are now seeing the systemic ways in which focused networks of conversation, especially with the support of collaborative technologies, can help organizations and communities evolve. Using The World Café as a methodology and as a metaphor offers a practical yet innovative way to cultivate both the knowledge required to thrive today and the wisdom needed to create the futures we want, rather than being forced to live with the futures we get.
Juanita Brown and David Isaacs serve as strategists and thinking partners with senior leaders, applying living systems principles to the evolution of knowledge-based organizations and large-scale change initiatives. They have hosted Café conversations and strategic dialogues internationally in a wide variety of business and community settings. (Contact info@theworldcafe.com or call 415-381-3368). The World Café Community is comprised of a growing global group of leaders and others committed to courageous conversations and positive futures. We thank Anne Dosher, Ken Homer, Susan Kelly, Janice Molloy, Nancy Margulies, Karen Speerstra, and Sue Wetzler for their special contributions to this article.
NEXT STEPS
-
-
- Notice the generative power of conversation and shared listening.
- Explore what you would do differently if you viewed your organization or community as a network of conversations and social learning through which we co-evolve the future.
- Consider how you might “seed” your own networks of conversation with questions that matter.
- Convene a Café conversation in your organization or community (for ideas, go to www.theworldcafe.com).
-
