As a global society increasingly becomes a reality and people strive to come together across divisions of culture, religion, race, age, gender, and other boundaries, it has never been more important for human beings to understand ourselves and each other deeply, to appreciate diversity while recognizing our essential commonalities, and to have tools for our intra- and interpersonal development. This is equally true in the context of organizational development. For organizational systems to work effectively, we need to understand in the first place the human systems that create and comprise them. Human Dynamics® provides the necessary framework of human understanding, together with developmental tools based upon it, for enabling the organization’s members to recognize, appreciate, and optimally utilize their diverse capacities, and work together harmoniously and productively.
What Is Human Dynamics?
Human Dynamics is a body of work that identifies and illuminates innate distinctions in the way people function as whole systems that include mental, emotional, and physical dimensions. It is the result of an ongoing investigation launched 24 years ago that has so far involved more than 80,000 people from over 25 cultures. From this research, we discovered that three universal principles – mental, emotional, and physical – combine in people in specific patterns characterized by distinctly different ways of processing information, learning, communicating, relating to others, solving problems, undertaking tasks, and, as a result, exercising leadership and contributing to groups or teams. These different “ways of being” appear to be so foundational in the human make-up that they can be seen the world over, identified at every age level (even in infancy), and observed in males and females equally. In other words, these distinctions are more fundamental to who we are and how we function than age, race, culture, or gender.
We have identified nine of these distinct human systems, or “personality dynamics.” Of these, five appear to be by far the most prevalent. The individuals representing these groups have characteristic gifts and affinities for certain ways of functioning. They flourish and contribute best under certain conditions. Most importantly, they have their own distinctive paths of development.
Being aware of and understanding these natural, inherent differences is significant for developing successful and effective human relationships of all kinds – for leading and partnering with others in the workplace, for developing loving and supportive family relationships, and for successful teaching and learning. When we don’t recognize and take into account these differences, we fall prey to misunderstanding others and misinterpreting their behavior; poor communication; less than optimum teamwork; and, in class and training settings, teaching approaches that do not “match” students’ specific learning processes. When we do understand the differences, the way is open for us to acknowledge and appreciate diverse ways of functioning; to see and adapt to others’ needs; and to relate, manage, and teach in ways that enable each group member to perform at his or her best. We are able to consciously utilize our own and others’ distinctive processes and capacities to achieve optimal individual and group performance.
The Three Principles
Let us first briefly explain what we mean when we refer to each of the three principles – mental, emotional, and physical. The Mental Principle is related to the mind. It is expressed in thinking, seeing things from a detached perspective, formulating a purpose or vision, seeing the overview, setting structure, and establishing principles and values.
The Emotional Principle is concerned with forming relationships. It is the subjective part of us that knows and values the world of feelings in ourselves and others; that needs and offers personal communication; and that relates, organizes, and collaborates. We express the Emotional Principle when we make new connections among diverse elements and exercise our creative imagination.
The Physical Principle is that part of us that is most down-to-earth and practical. It is expressed in making, doing, actualizing, and operationalizing. The Physical Principle has to do with the realm of the senses, rather than that of the mind or the emotions. It is concerned with understanding the operation of systems, both natural and human-made, and with creating effective systems of operation.
All of these dimensions are active in all people, but to varying degrees and in various combinations (see “The Mental, Emotional, and Physical Principles”).
THE MENTAL, EMOTIONAL, AND PHYSICAL PRINCIPLES

It is also important to note that each of these principles is of equal value. They are all needed in the functioning and development of a whole and balanced person. We could also say that all are equally needed for the functioning of a whole and balanced organization.
At this point, pause and ask yourself, “With which of these principles am I most comfortable and familiar? Which do I express most easily and naturally? Could I benefit from some development or help with one of these areas?” As we shall see, individuals are generally more comfortable and familiar with two of the principles, while the third is often less known, developed, and utilized.
Mental, Emotional, and Physical Centering
While all of us have mental, emotional, and physical dimensions, we have discovered that people seem to be “wired” in such a way that one of these three principles is central in each individual’s functioning. People are “centered” mentally (rationally), emotionally (relationally), or physically (pragmatically) (see “Centering”).
Of course, each human system comprises a continual interplay of mental, emotional, and physical life. Nevertheless, each person is characterized by a central process that is specific and consistent. The principle at our core determines how we typically take in and process information.
Mentally centered people process information in a logical and sequential way. They are also characterized characterized by an innate detachment. They experience life as if they were standing on a hilltop, so they naturally maintain a birds-eye view on events and a long-term perspective.
Emotionally centered people, on the other hand, process information in a non-linear, associative, interactive way that incorporates feelings and intuition, rather than through a strictly rational process. This relatively spontaneous way of proceeding often results in the generation of new ideas and the exploration of new avenues of thought or action that might not have emerged through a more linear process. For emotionally centered people, engaging in dialogue with others is essential as a means of clarifying thoughts, feelings, and intuitions, as well as for establishing the sense of personal connection with others that makes life meaningful for them.
Finally, physically centered people process information in a systemic way – they gather and assimilate large amounts of data, and think in terms of the interconnections that make up whole systems of functioning. Because of their affinity for the systemic, they may be fascinated by the patterns they observe in the flow of events across time, from past to present and projected into the future, or they may have a keen interest in, and sense for, how things work mechanically.
Five Predominant Personality Dynamics
We have found that there are three variations on each of these major themes. Mentally centered people may be “mental-mental,” “mental-emotional,” or “mental-physical.” Emotionally centered people may be “emotional-mental,” “emotional-emotional,” or “emotional-physical.” And physically centered people may be “physical-mental,” “physical-emotional,” or “physical-physical,” making nine personality dynamics in all. Whereas the first principle indicates how one processes information, the second indicates what one processes – the kind of material that is the natural focus of attention. (This interaction will become clearer when we outline particular personality dynamics.)
CENTERING
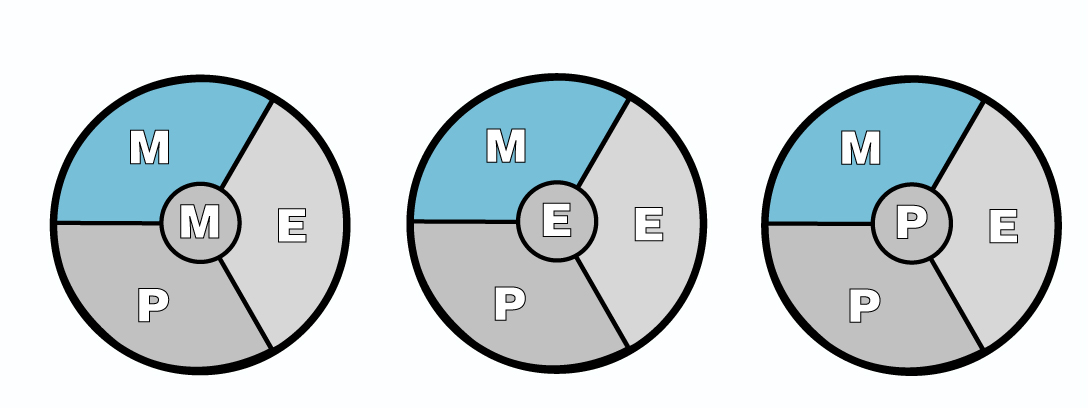
While all of us have mental, emotional, and physical dimensions, people seem to be “wired” in such a way that one of these three principles is central in each individual’s functioning. People are “centered” mentally (rationally), emotionally (relationally), or physically (pragmatically).
Of these nine possible systems of functioning, we have found that five are by far the most prevalent – mental-physical, emotional-mental, emotional-physical, physical-mental, and physical-emotional. Any group of people – the members of a management or project team, a department, the students in a classroom, family members seated around the dinner table, a meeting of heads of state – will include some combination of these five different ways of being “wired,” with their distinctly different natural processes of learning, communicating, problem-solving, relating, developing, and so on.
Following are brief thumbnail sketches of each of these five most commonly encountered personality dynamics. These summaries provide a basic sense of their similarities and distinctions, and also of the misinterpretations of each that commonly arise as a result of their particular ways of functioning.
Mental-Physical. As we have already indicated, the thinking process of mental-physical people is linear, logical, and sequential (mental principle), and it is focused upon operations in the external world (physical principle) – as opposed to emotional data. Because of their “hilltop” perspective, they tend to focus on the long term and to think in relation to enduring principles and values. Because of their innate detachment, their emotional life is typically extremely even. Mental-physical people offer teams emotional stability, objectivity, and their gift for selecting and articulating what is essential – key points, principles, values, goals, and information. They value clarity; for this reason, they often prefer written communication. They are usually precise and meticulous in any task that they undertake.
Mental-physical people often ask the questions “Why?” and “What do you mean by…?” But they are frequently silent in groups, either because they feel no need to speak if others are saying what needs to be said, or because they think carefully before speaking and cannot find the space to participate if a process is less than orderly. Because of their natural detachment and reticence, and because they do not readily express their feelings, others may interpret mental physical people as being aloof, disengaged, uncaring, or unwilling to be approached. None of these interpretations is necessarily true. If you want to know how a mental-physical person is really thinking or feeling, just ask. Such questions will help him or her to connect and communicate.
Emotional-Mental. Emotional mental people process in a non-linear, associative way (emotional principle) the world of ideas (mental principle). They deeply enjoy a highly interactive brainstorming kind of communication, in which one idea triggers another, leading to the generation of new ways of thinking or acting. Emotional-mental people typically love movement and change. They are often innovators, drawn to the new and untried. They intuitively sense new possibilities in people, situations, and events, and endeavor to make them happen.
In undertaking new projects, emotional-mental people can move into action with the strong sense of a general direction to be taken, but with minimal data and little or no real prior planning. This experimental movement leads to new experiences, which suggest next steps that may be entirely unanticipated at the beginning. They repeat this process until they reach a satisfactory outcome.
Because emotional-mental people concentrate on the future, they typically recollect very little about the past. They do, however, remember data required for any project that is their current focus of attention – but only until the project is completed. Emotional-mental people usually have little awareness of physical signals from their bodies. They may be able to work long hours with great concentration because they are unaware that they are hungry or tired.

Others may misunderstand emotional-mental people as being either pushy or, because they will initiate movement with little or no prior planning, irresponsible. Instead, they are following their natural instinct to move things forward and light the fires of new endeavors, often relying on others to execute the details.
Emotional-Physical. Emotional-physical people also think in a non-linear, associative way (emotional principle), preferably through dialogue with others, but their focus is on the physical world (physical principle) – especially people! They experience constantly changing emotional responses to their environment and all the objects, people, and events in it. They are sensitive to others’ feelings and often can sense those feelings in their own bodies, even when others aren’t outwardly expressing them. This ability can be a gift, providing helpful information and insights; it can also be a burden, affecting the emotional physical person’s sense of well-being in negative circumstances, or creating confusion about whether feelings experienced are his or her own or those of someone else.
Emotional-physical people value personal connection and communication with others. They bring to teams both a high degree of creative thinking and a concern for creating harmony among group members. The quality of the group’s process is as important to them as the outcomes. However, they can only offer their full capacities if they feel comfortable and “safe.” If they feel threatened or judged in any way, they may withdraw and stay silent.
Emotional-physical people can relive emotion-laden events from the past as if they were occurring again in the present. Sometimes others judge them as “too sensitive,” “using too many words,” or insufficiently logical. The truth is that their sensitivity is a gift to be valued – they use it for understanding individuals and interpersonal situations. Their sometimes extensive communication results from their need to establish personal connections and to ensure that misunderstandings don’t arise. And their non-linear thinking has an emotional logic, frequently reflecting a “knowing” that they cannot rationally explain. Their intuitive gift is often a wasted resource in organizations.
Physical-Mental. Physical-mental people think systemically (physical principle), with a focus on ideas, purposes, and structures (mental principle). They plan consciously, strategically, and systematically. They want to know the purpose of any endeavor and then create a logical step-by-step plan for achieving that purpose. They tend to have a conscious strategy for almost everything they do.
Physical-mental people value efficiency and create systems of operation to achieve it, then refine those systems to make them even more efficient and, if possible, broadly applicable. They like to use models, diagrams, and charts to assist their thinking or communicate their ideas. Physical-mental individuals gather considerable data as a basis for their planning and put it into logical structure quite quickly. They have a capacity for seeing patterns in varied data or in the flow of events, from which they make projections into the future and devise action plans.
Physical-mental people have a detailed memory for data in areas that interest them. In communicating with others, they are always looking for the action to be taken or problem to be solved. They like communication to be factual and organized.
A common misunderstanding about physical-mental people is that they do not care about people or their feelings. This misperception can occur because they may be so focused on results that they may sometimes fail to consider human factors in their planning. Also, they usually find it difficult to express personal feelings. They typically express their caring through their actions rather than their words.
Physical-Emotional. Physical-emotional people process in a systemic way (physical principle) the connections (emotional principle) among data, events, and people in order to comprehend or create whole systems of operation. Their natural process of thinking, planning, and learning is not systematic but organic. When approaching any new endeavor, they immerse themselves in gathering and absorbing data without initially sorting or prioritizing it. (Because for them everything is connected to everything else, they do not always know initially what might be relevant). They then assimilate, sort, and link all of this information in a process that may be as much unconsciously as consciously directed. This process, like digestion, takes its own time, until suddenly everything comes together in a highly detailed, systemic understanding of a situation, plan of action, or product. Because the entire process takes place internally, others may think that “nothing is going on,” when in fact very much is “going on,” though the person may not be able to clearly articulate what it is until the process is complete.
Physical-emotional people are sometimes labeled “slow” in a negative sense. In classrooms they may be categorized as “slow learners,” with the implication that they may not be as smart as other students who respond more quickly. They are not really slow at all, but rather thorough. Their organic process takes time, but they are typically able to assimilate and synthesize more data and comprehend and handle more complex situations than people of any other personality dynamic.
Physical-emotional people typically have a prodigious capacity to remember data. They can recollect events from even the distant past in which they were fully engaged in extraordinary sensory detail. Because physical-emotional people think and experience in terms of interconnections, they appreciate communication that provides “the whole story,” and they often convey information through detailed stories.
Distribution of Personality Dynamics
The personality dynamics that we have identified are not equally prevalent or evenly distributed. Of the five dynamics that we have described, mental-physical people are encountered most rarely – they seem to constitute no more than about 3 percent of the population. The great majority of the world’s people appear to be either emotionally or physically centered.
Anyone of any personality dynamic may be more or less intelligent, more or less compassionate, more or less contributive, more or less gifted.
It has been fascinating for us to experience over the years that in the Western cultures in which we, or the facilitators we have trained, have worked extensively (such as North America, Europe, South America, and Israel), we have found a slight majority of people to be emotionally centered and the rest to be physically centered. In Eastern countries in which we have worked, such as Malaysia, China, Singapore, and Japan, we have found by far the great majority of the people to be physically centered. These findings apply even to people of Asian descent whose families have lived in the West for many generations.
We have no explanation for the fact that the two physically centered personality dynamics seem to predominate in the East and the two emotionally centered ones in the West. We simply offer our findings. However, we emphasize that no value judgments adhere to this observation. All of the personality dynamics are equal in value. It is not “better” to be one more than another. Anyone of any personality dynamic may be more or less intelligent, more or less compassionate, more or less contributive, more or less gifted. What is different is how they “are,” think, experience, and go about things. Indeed, we can say that each needs the others for results that are optimal and whole.
Nature vs. Nurture
We have often been asked if we think that this distribution of personality dynamics could be the result of cultural influence. Our experience has led us to believe otherwise, for a number of reasons:
The cultural explanation does not account for the many physically centered people in the West or the emotionally centered people in the East.
If culture created the personality dynamics, then one would expect the many people of Asian background who have been assimilated over generations into Western cultures, and who are not part of an Asian community within the larger community, to show the characteristic processes of the majority in their adoptive cultures. However, we have not observed this to be the case. Although many Asian Americans, for instance, may have adopted more characteristically Western values, their foundational processes of handling information, learning, problem-solving, and so on remain those characteristic of physical centering.
We have come up with the same findings in following infants adopted from the East into families in the West in which both of the adoptive parents were emotionally centered. As these youngsters develop, they may exhibit their parents’ influences in some aspects of their outer behavior – for example, by being somewhat more expressive of their feelings and individually oriented than is typical of their Asian-raised counterparts – but their fundamental processes remain those we have described as characteristic of physical centering.
The evidence indicates, therefore, that while there is a continual interaction between any individual’s personality dynamic and the external environment, the latter neither determines the basic natural processes nor fundamentally alters them. It may influence what one thinks or learns, but not how one naturally thinks or learns.
We are led to assume, therefore, that the distinctions we have identified are inherent and genetically determined. This conclusion is reinforced by our findings that people almost always identify at least one parent as having the same personality dynamic as themselves or, if not, a grandparent.
Implications for the Workplace
These different ways of being and functioning are represented wherever people live, learn, and work together. They are present in every work environment, among management and project teams, in boardrooms and training rooms, in meetings with staff or potential clients, in conference calls with colleagues or strangers from around the globe, and, of course, in classrooms (see “Human Dynamics in Education”). It has been said that 90 percent of the difficulties that organizations face can be attributed to dysfunctional relationships among people. When people develop awareness and understanding of the different personality dynamics, much interpersonal misunderstanding and conflict is avoided. Also a groundwork is laid for developing optimal communication, teamwork, coaching, mentoring, and training. A shared base of understanding enables colleagues to work together more effectively and to consciously leverage one another’s gifts and capacities.
HUMAN DYNAMICS IN EDUCATION
For example, at the beginning of the school year, students discuss with the teacher-facilitators and their parents what they will learn during the year. Then each day students decide individually how they will learn. The day begins with a period of relaxation during which students listen to music to quiet and “center” them. This may be followed by a period of conventional group instruction. Then students are free to follow their own self-study plans. They work alone, in pairs, or in groups as they wish, and move from one learning environment to another as meets their needs. The teacher-facilitators, with deep understanding of each child’s needs and processes, are available as supporters and coaches. They also keep a meticulous record of each student’s progress toward the established goals and meet with each student daily to discuss progress and possible new goals or strategies.
Because they know their own and each other’s personality dynamics, and have worked to develop themselves, the teacher-facilitators have created harmonious working relationships. They also have close relationships with the parents, who are involved in the planning process and attend Human Dynamics presentations. Teacher-facilitators, parents, and students thus share both a common endeavor and “a common language” for communication and mutual understanding.
A conscious goal of this facilitative approach is that students become aware of and value their own processes (including learning) and their associated gifts, capacities, affinities, and developmental needs. Not only do they feel highly affirmed, but they become equipped with fundamental self-knowledge that will serve them throughout their lives. They also learn how to support and complement the processes of other students. As a result, these classrooms have become highly motivated, conscious, deeply respectful, and mutually supportive learning communities, in which each student participates and functions in accordance with his or her natural design.
Needless to say, to conduct this kind of organic learning environment requires deeper training and an even higher degree of behind-the-scenes organization than the standard “delivery of instruction.” But the rewards are infinitely greater in terms of the learning achieved and the satisfaction both teachers and students experience in a classroom where truly “no child is left behind.”
NEXT STEPS
- Discuss with other team or family members why you think you might be a certain personality dynamic.
- Think about how you like information to be given to you or how you like to communicate or be communicated with, and let others know. Ask others about their needs.
- Think about other family or team members: Is it possible you may have misunderstood or undervalued some things they do or how they do them?
- Consider how you express the three Principles in your own life. If one is less developed, what might you do or practice to strengthen it?
- In the course of our lives, we often learn to conform to the prevailing culture and behave in ways that are not natural to us. Doing this can hinder us from accurately identifying our personality dynamic. It may help to ask yourself, “How was I as a child?” or “What would I have liked my parents or teachers to have known about me that they seem not to have understood?”
Sandra Seagal and David Horne are the founders and directors of Human Dynamics International, an organization that disseminates unique training programs in the fields of organizational development, education, healthcare, and cross-cultural bridge-building. They are also the founders and directors of the Human Dynamics Institute, which is engaged in original research into the personal, interpersonal, and transpersonal functioning and development of people. Sandra and David are coauthors of Human Dynamics: A New Framework for Understanding People and Realizing the Potential in Our Organizations (Pegasus Communications, 1997) and are working on a new book directed toward parents, teachers, and all who care about children. For more information, go to www.humandynamics.com.
